
ΑΙhub.org
#ICLR2022 invited talk round-up 1: AI for science – protein structure prediction
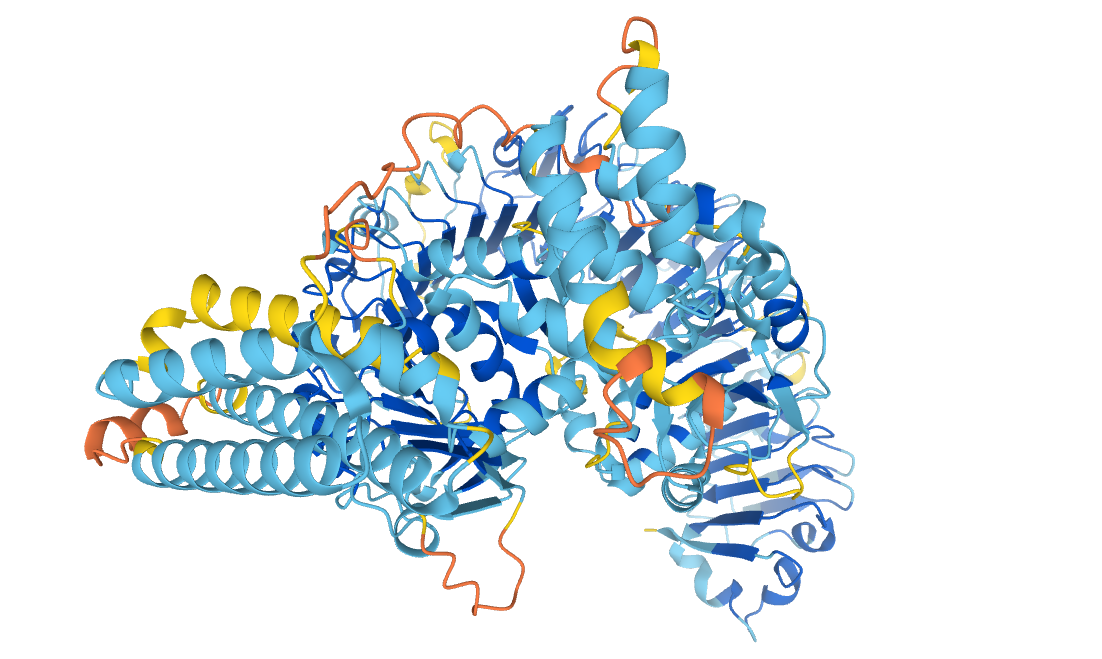 Probable disease resistance protein At1g58602, from the AlphaFold Protein Structure Database, reproduced under a CC-BY-4.0 license.
Probable disease resistance protein At1g58602, from the AlphaFold Protein Structure Database, reproduced under a CC-BY-4.0 license.
This year’s International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) boasted eight invited talks on topics ranging from reinforcement learning to connectomics, from societal considerations to interpretability. In this article, we summarise the talk given by Pushmeet Kohli.
Leveraging AI for science
Pushmeet Kohli, DeepMind
Around five years ago, the DeepMind team started a science programme with the aim of using AI to pursue breakthroughs in impactful science challenges. In his talk, Pushmeet talked a bit about their approach, and focussed on the case study of AlphaFold2, which made a huge advance in the field of protein structure prediction.
Science offers many challenges and opportunities for AI. Through a variety of different experiments, such as high energy physics and genomics, there is a vast amount of data being produced. Many experiments are extremely complex and require a high-level of control. When it comes to scientific models, there is generally a high level of complexity and sophistication, a good example being in weather prediction. These are aspects (data, control, complexity) in which AI could play a key role in helping to advance different scientific disciplines.
Pushmeet highlighted three important elements of science, which also need to be considered when producing AI models. These are: generalisation (theories ideally hold universally), uncertainty prediction (we need to know how confident can we be about trusting a model), and explanability/interpretability.
Case study: Protein structure prediction with AlphaFold2
Proteins are large, complex molecules, and the shape of a particular protein is closely linked to the function it performs. The ability to accurately predict protein structures would enable scientists to gain a greater understanding of how they work and what they do. This close link between structure and function has been a key driver behind the problem of protein structure prediction.
It is extremely difficult and time-consuming to determine a protein structure experimentally. Typically this could take a researcher a year or more, just for one structure. By having an accurate prediction, this process could be greatly accelerated.
 Screenshot from Pushmeet’s talk.
Screenshot from Pushmeet’s talk.
In 1994, the community-wide experiment for protein structure prediction, Critical Assessment of protein Structure Prediction (CASP), held its first biannual competition. CASP provides an independent mechanism for the assessment of methods of protein structure modelling and teams of researchers take part to see who can provide the most accurate predictions. In the 2020 experiment, AlphaFold2 achieved a significant jump in performance as compared to previous years.
The AlphaFold2 architecture takes in an amino acid sequence, performs a genetic database search to find known structure of related proteins, and completes multiple sequence alignments. Sequence alignment is a way of arranging the sequences of proteins to identify regions of similarity. It then takes all of this information and feeds it to a neural network (with a transformer-type architecture) which works with a pair representation (considering the relationships between all the pairs of animo acids) and a multiple sequence alignment (MSA) representation. Finally, there is a structure module which outputs the final structure. You can read more about the method in the team’s 2021 paper: Highly accurate protein structure prediction for the human proteome. Another important facet of AlphaFold2 is that it does not only make structure predictions, it also predicts how much uncertainty/confidence there is for a particular prediction.
Pushmeet stressed that what enabled this work was the large collection of past data and research knowledge from years of previous study on protein structure, principally by the experimental biology community. He noted that resources such as the protein data bank, and the founding of CASP have been critical for the development of protein structure prediction methods.
To close his talk, Pushmeet briefly mentioned a number of other science problems that the team are working on. These include magnetic confinement control of plasmas for fusion, functional genomics, AI for mathematics and quantum chemistry.
tags: ICLR2022










