
ΑΙhub.org
Rewarding explainability in drug repurposing with knowledge graphs
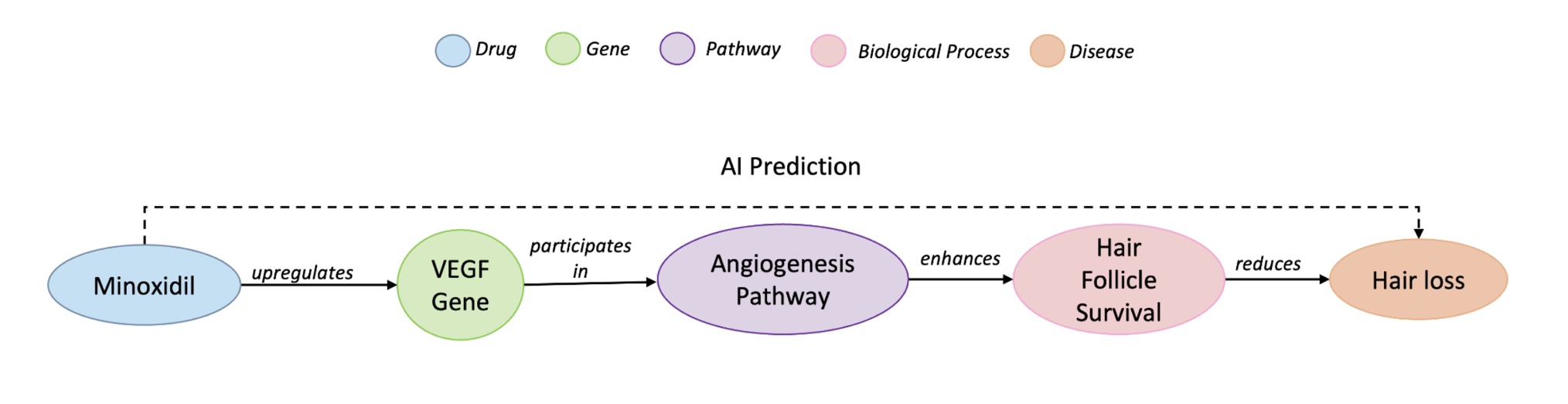
Drug repurposing often starts as a hypothesis: a known compound might help treat a disease beyond its original indication. A good example is minoxidil: initially prescribed for hypertension, it later proved useful against hair loss. Knowledge graphs are a natural place to look for such hypotheses because they encode biomedical entities (drugs, genes, phenotypes, diseases) and their relations. In KG terms, that repurposing can be framed as a triple (minoxidil, treats, hair loss). However, many link prediction methods trade away interpretability for raw accuracy, making it hard for scientists to see why a suggested drug should work. We argue that for AI to function as a reliable scientific tool, it must deliver scientifically grounded explanations, not just scores. A good explanation connects the dots through established biology (e.g., upregulating VEGF enhances hair follicle survival).
From predictions to explanations
Our work introduces REx, a reinforcement learning approach that not only predicts which drug-disease pairs might hold promise but also explains why. Instead of optimizing purely for accuracy, REx trains an agent to traverse a biomedical knowledge graph while being rewarded for producing paths that are both faithful to the prediction and scientifically relevant.
A path is considered faithful when it successfully connects the drug to the disease under investigation, and relevant when it involves specific, informative biomedical entities rather than generic ones. To measure this relevance, we developed a new metric based on Information Content (IC), which favors more specific biological concepts such as “VEGF signaling pathway” over broad ones like “cancer.”
This reward mechanism encourages the model to search for concise and meaningful reasoning chains, similar to how a researcher might connect experimental evidence across different domains. As a result, REx shifts the focus from “Can we predict this link?” to “Can we justify this link scientifically?”
How REx works
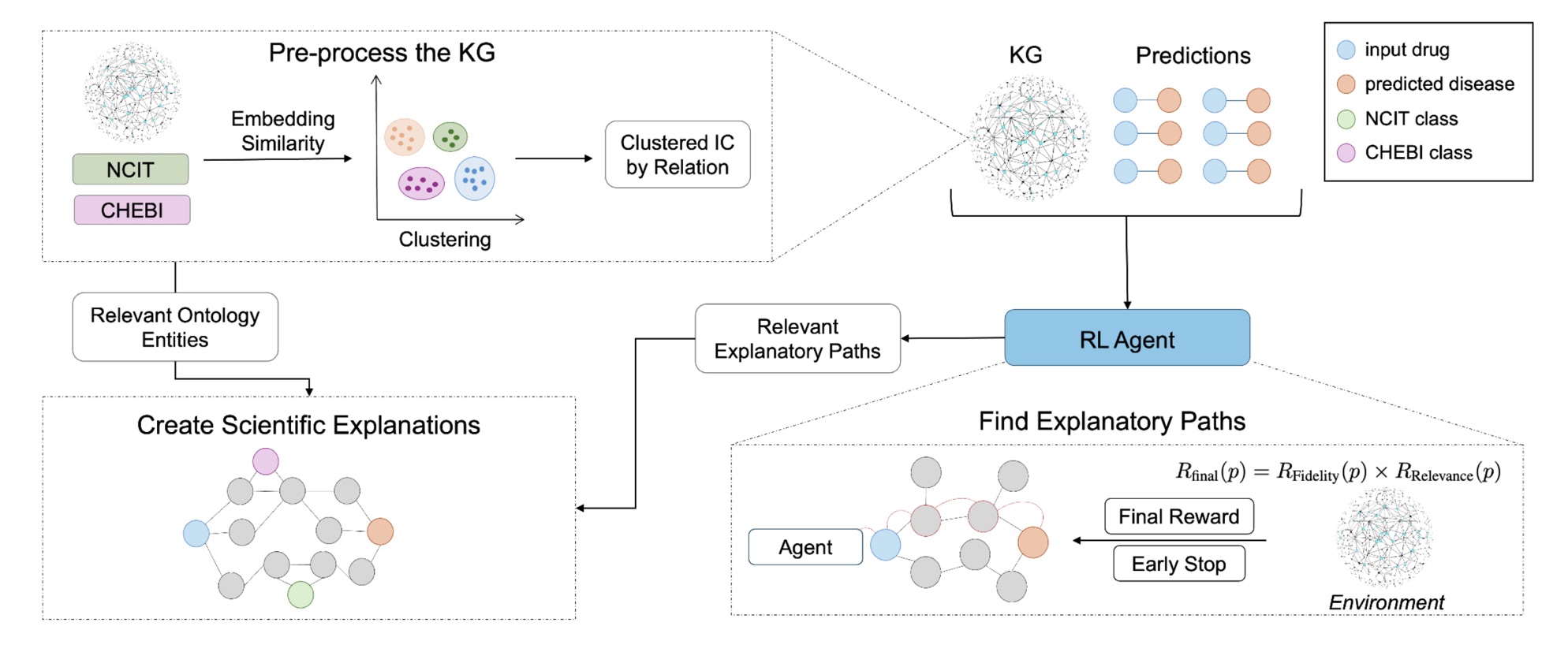
REx trains a reinforcement learning agent to explore the biomedical knowledge graph one step at a time, moving from the drug node toward the disease node. At each step, the agent decides whether to follow an outgoing relation (for example, interacts_with or regulates) or to stop if it has reached a meaningful endpoint.
To encourage scientifically sound reasoning, the agent’s reward combines two signals:
- Fidelity: whether the path successfully reaches the target disease.
- Relevance: how informative the path is, based on the average information content of its entities.
By multiplying these two rewards, REx ensures that the highest-scoring explanations are both correct and insightful. The model also includes an early-stopping mechanism: once the disease node is reached, the agent halts instead of wandering into redundant connections.
Once relevant paths are found, REx groups them by metapath pattern: their structural type of reasoning (for instance, drug → gene → disease). It then merges the best representatives of each pattern into a compact explanation subgraph. To add biological context, REx enriches this subgraph with ontology terms from the National Cancer Institute Thesaurus (NCIT) and the Chemical Entities of Biological Interest (ChEBI), ensuring each explanation aligns with well-defined biomedical concepts.
Why this matters
REx doesn’t just present predictions, it helps scientists understand them. By rewarding both accuracy and biological relevance, REx finds reasoning chains that mirror scientific thinking. This makes it possible to validate AI-generated hypotheses, not just generate them. In drug repurposing, that distinction is crucial: a prediction is useful only if we can understand why it might hold true.
By turning explainability into a rewardable objective, REx shows that interpretability and performance can reinforce each other, rather than compete.
Future directions
Like most systems built on knowledge graphs, REx’s reach depends on the completeness of available data. As biomedical graphs grow richer, we expect the explanations to become even more detailed and accurate.
We are now extending REx beyond drug repurposing to related areas such as drug recommendation and drug-target interaction prediction. Across all these domains, the goal remains the same: to make AI systems that can reason and explain to scientists.
Available resources
This work was presented at IJCAI2025.
tags: IJCAI, IJCAI2025












