
ΑΙhub.org
Architecting a privacy-preserving dialogue system software development kit
By Gerrit Klasen
Use of dialogue systems such as Alexa, Siri, and Google Assistant raises several questions. In recent years, these virtual personal assistants have become the most popular representatives of their field. Although the quality of the communication and the supported languages is improving day-by-day, there are still several concerns.
As reported in one of our previous posts, one of the most important concerns is privacy. The lack of transparency of some of these systems raises the question whether, and for how long, sensitive user content is stored in the cloud and for what further usage. In the event that this personal information is shared with third parties, it could be used to create user profiles. These profiles could be exploited in both legal (e.g. recorded buying behaviour may be reused to customise advertisements presented to the user) and illegal (e.g. sensitive information like health data, passwords, and some other contents could be used to blackmail victims) ways. These threats only represent a small number of the possible personal data abuses. With technological advances and the increasing number of people and apps using dialogue systems, the privacy concerns in dialogue systems are escalating. Every app published with current dialogue system solutions adds an additional risk into the app stores.
Therefore, a fully private-by-design methodology must be adopted for the design of software solutions integrating dialogue systems. To facilitate this, privacy-preserving features should be made available via a Software Development Kit (SDK). The SDK should provide an easy-to-use interface to enable developers to easily include the required privacy-aware functionalities in their applications. But what are the components needed to fulfil such a requirement?
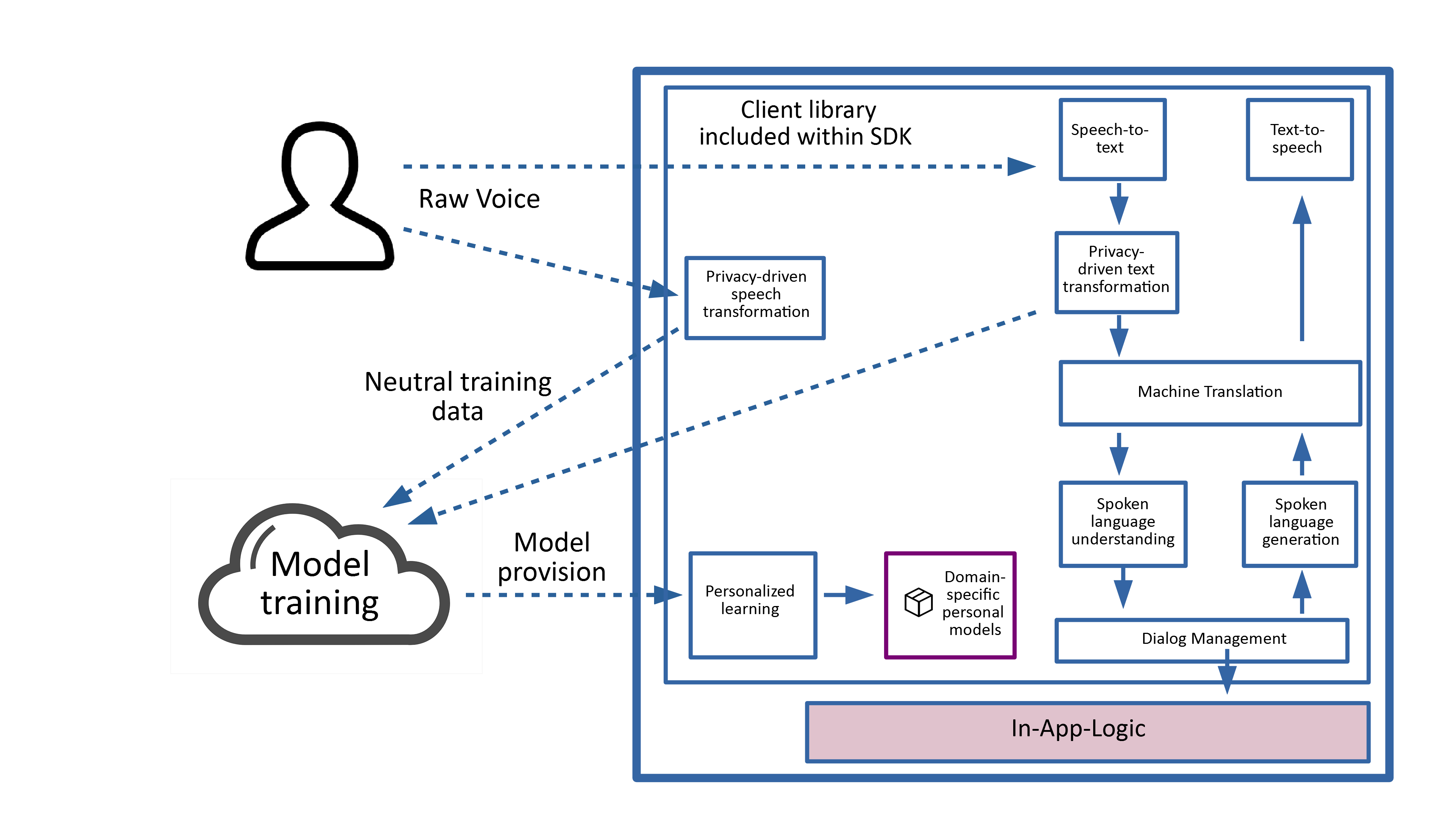
Before digging into this, note that, at first glance, the idea of a fully-private-by-design methodology seems to be in conflict with the goal of dialogue systems. This is because modern dialogue systems are trained on real user data and, in order to do so, this data must be stored in the cloud. The more data can be collected, the better the quality of the communication will be in the future. Stating that, a privacy-preserving dialogue system should protect the user’s private data, and at the same time it should not prevent sharing voice data for training purposes. To fulfil both of these constraints, the dialogue system needs a component which can filter sensitive information from the spoken content, before it’s sent to the cloud. To ensure that an app still executes the intended voice command, the private information isn’t deleted entirely, but saved locally onto the device for a short duration until the command is executed.
As an example, such a system can anonymise the content in two complementary ways:
- Using a privacy-driven voice transformation to neutralise acoustic content. For instance, this transformation could modify the user’s voice into that of a random user and ensure that it has a neutral timbre. This will ensure that third parties cannot identify the user or infer characteristics such as gender, ethnicity or health issues from the user’s voice.
- Using a privacy-driven text transformation to neutralise the actual information after speech-to-text. For example, this transformation could take the speech-to-text output “I, Max Mustermann, need Dextroamphetamine” and replace private information, namely the user name and the medicine name, by random information such as “I, John Doe, need Doxycycline”.
The neutral content has enough information for dialogue system training, and can now be sent to the cloud without any doubts or fear. At the same time, the original information saved locally can still be used to trigger specific application behaviour such as ordering “Dextroamphetamine” in the above example. The strategy of privatising voice and text content for cloud-based training while retaining private information locally should be made accessible to as many people as possible. Only publicly accepted and widespread ideas within the SDK and their outcoming application solutions can have a real impact, both for end-users and software developers.
In order to achieve a large user base, the SDK should include a privacy-preserving dialogue client that provides the same performance for both widespread languages as well as less popular ones. The problem with the latter is that often the training datasets are too small to correctly interpret the user commands, which leads to poor or misleading communication. One idea to address this problem is to train dialogue models for the most widespread languages only (e.g. English) to ensure decent communication, and to allow machine translation into English from different languages without hurting privacy. To fulfil this vision, the library should also include a multi-language speech-to-text component. This component shall operate locally on the client device to prevent voice data being sent to the cloud before privacy-driven text transformation has taken place. After these steps, cloud machine translation APIs would be accessed and even allowed to translate text. This would allow Hindi as an input, for instance, to be translated into English and therefore interpreted with a much larger set of natural language understanding models, which leads to better dialogue management reactions and natural language generation, as seen in our previous post. The well-defined answer generated by the system would then be translated back from English into the original language, here Hindi. Such an architecture ensures privacy, but also allows niche languages to be interpreted to a high quality.
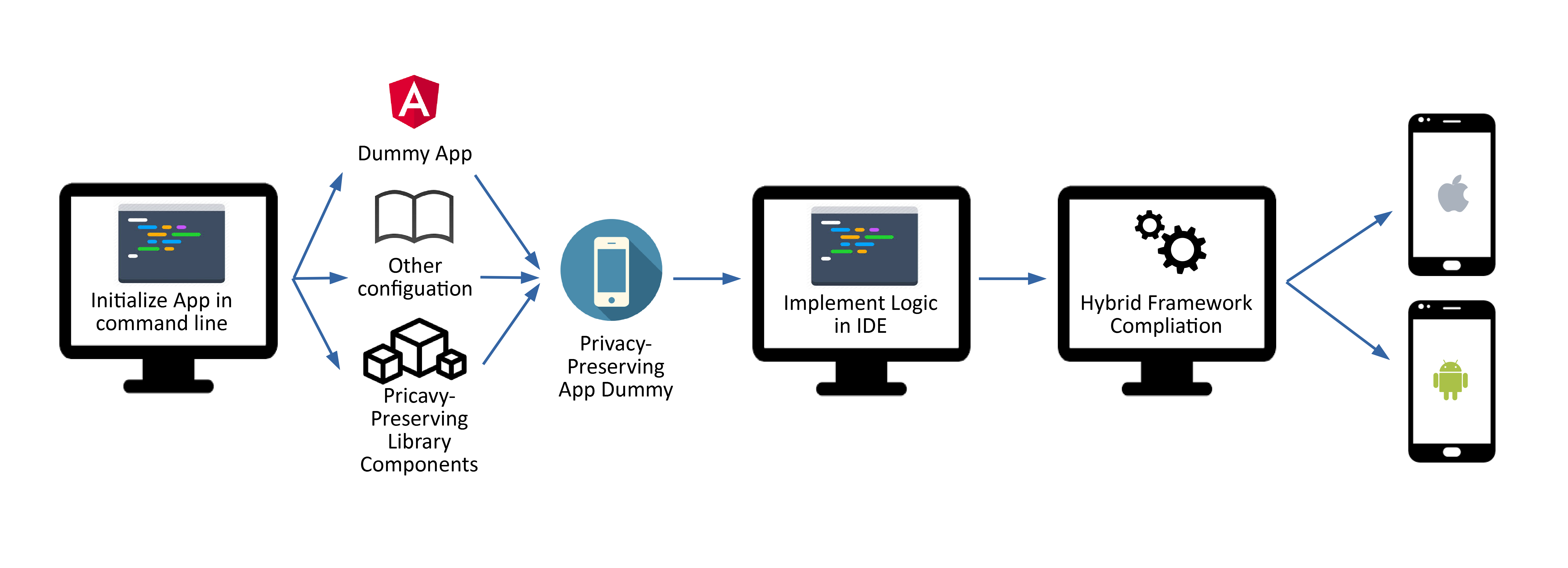
Eventually, we not only want to ensure a bigger target group, but also to provide software developers, as stakeholders, with the required software components more easily. Simple command lines provided by the SDK shall trigger the inclusion of all necessary components into a final app. This would be an easy one-click-generation of privacy-aware dialogue system apps, which the developer can then extend with his/her own programmatic logic in any development environment. A second way to maximise the output with minimal input is the use of hybrid development frameworks, which allow cross-compiling of the input to multiple platforms like Android and iOS. Regarding the training of the dialogue models, via the SDK developers could also access an API to various cloud services which allow the training and initialisation of application-related, dialogue system models. In addition, after developers have configured the models with the help of a cloud platform-based access interface, they could be loaded onto a personalisation module at runtime in order to further adapt answers for the user.

To sum up, it is possible to tackle privacy problems within virtual systems. By defining an architecture which can remove private information locally on the user’s device both in speech and text, we allow dialogue systems to receive sufficient training data and still ensure user privacy.
The provision of personalisation components exploits the fact that private information must be stored locally for a short duration in order to ensure that the actual app behaviour (e.g. ordering) still works fluently and that this information is not lost after anonymisation. Translating every input language into a single language and back enables such a system to support more languages while ensuring a high-quality interpretation of user intent. Hybrid frameworks used in the scope of the SDK extend the multi-language support with a multi-platform support, to enable a large user base, as well as empower developers to deal with an easy-to-use SDK.
For further technical details, we invite you to refer to our deliverable D5.2 – Platform hardware and software architecture, and to D4.1 – SDK software architecture.










