
ΑΙhub.org
Neural approximate dynamic programming for on-demand ride-pooling
In this post Sanket Shah (Singapore Management University) writes about his ride-pooling journey, from Bangalore to AAAI-20, with a few stops in-between.
Before joining Singapore Management University (SMU), I lived in my hometown of Bangalore in India. It is a city that, much to my chagrin, has become synonymous with its terrible traffic. The absence of comprehensive public transport has meant that, often, the most convenient alternative to owning a vehicle is using taxi-on-demand services from aggregators like Uber and Ola. The affordability of ride-pooling services (like UberPool) have made them especially integral to the transportation ecosystem with taxi-sharing often being the cheapest means of on-demand transportation. However, while ride-pooling services are popular, they are far from efficient. I would often find myself trapped in circuitous two-hour long UberPool journeys, obsessing over ways to do things better. As a result, when an opportunity to work with my current advisor on such ride-pooling systems presented itself, I jumped at it.
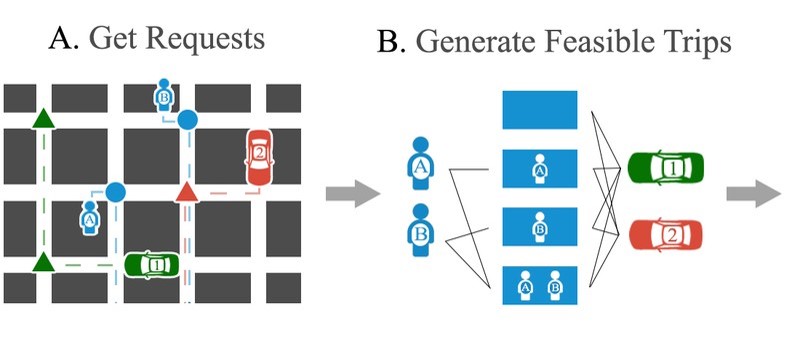
At SMU, I started thinking of solutions to this problem in earnest—how do you match customers to vehicles so that people would no longer have to circumnavigate Bangalore on their way to work. With lots of help from my collaborators, I went through the literature, especially the erstwhile state-of-the-art method for high-capacity city-scale ride-pooling ‘On-demand high-capacity ride-sharing via dynamic trip-vehicle assignment’. In this approach, they enumerated the feasible assignments of passengers to a vehicle and then ran an optimisation over these feasible assignments to choose the best combination of assignments over all vehicles. The time-consuming portion of this process was in enumerating these feasible assignments because there are an exponential number of them (in the worst case) and each involves solving an NP-hard routing problem. As a result, in practice, one can only generate a subset of all the feasible assignments.
Accordingly, given that all feasible assignments can’t be enumerated, our first attempt at improving their solution was in trying to generate a ‘better’ subset of them. We did this by ‘learning to search’, which is similar to A* search in which the heuristic is learned. The novel idea here was to make learning this heuristic unsupervised by using the weak supervision from the output of the optimisation problem—we scored assignments based on how likely they were to be chosen as the optimal assignment. We found, however, that enumerating ‘better’ (or even more) assignments didn’t improve the solution quality much. Instead, from visualising some trajectories, we found that a bigger issue was that the optimisation was greedy, i.e., it tried to maximise the matches at the current time-step without thought for how this would affect future matches.
To solve this problem, during the optimisation step, we tried to score the enumerated feasible assignments based on their expected future value rather than their immediate value. This idea has connections to learning a value function in the Q-Learning approach to RL, in which the optimal policy involves choosing the ‘action’ (overall assignment) with the maximum future value. The key insight was that, if we could find a way to estimate this future value for a given feasible assignment, we could use the existing optimisation over feasible assignments to approximate this ‘max’ operation in Q-Learning. Along these lines, I developed an algorithm for estimating this future value of a feasible assignment and tested it on real-world data – it worked! We found that it outperformed the greedy method by up to 16 % (which is huge on a city-scale).
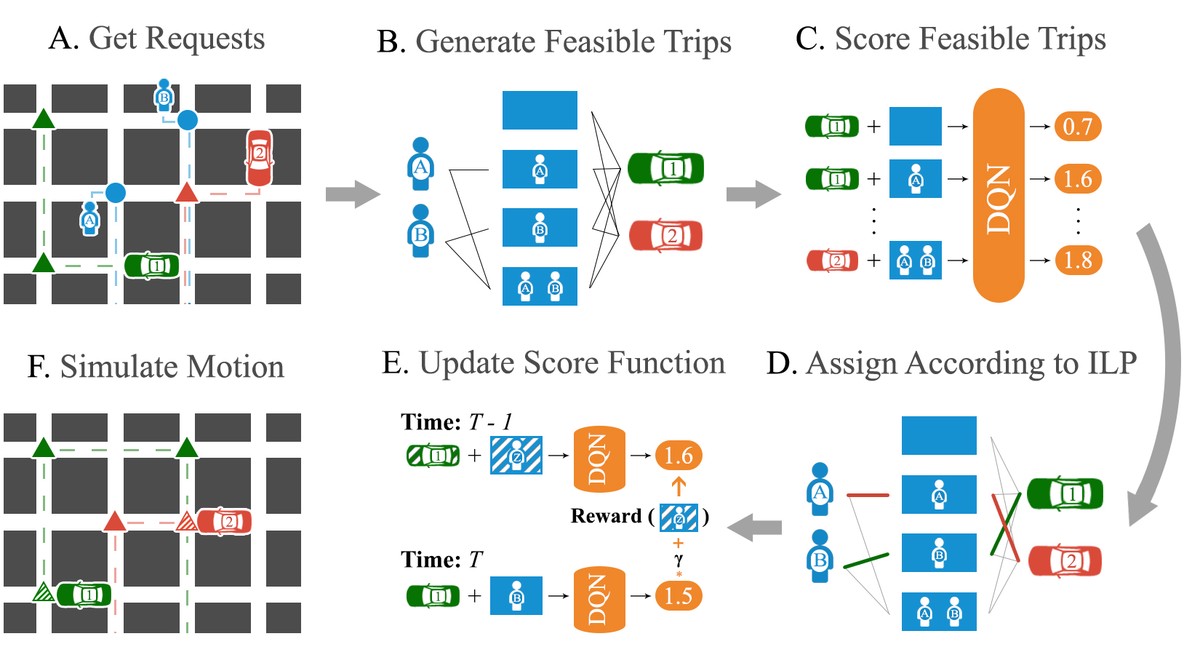
This is where I thought the project would end. However, we hit a surprising roadblock – we learned that, although the algorithm was ‘inspired’ by Q-Learning, the modifications we made to it meant that it was no longer straightforward to use the theoretical results associated with Q-Learning to illustrate the soundness of our algorithm. The final part of this project involved finding a more ‘natural’ way to communicate what the algorithm was doing and why it worked. To this end, we did some reading and found that we had re-invented Approximate Dynamic Programming (ADP), a framework from Operations Research that could be seen as a way to combine traditional optimisation with learned value functions to perform stochastic planning. The discovery allowed us to use the language and theory that they had (much more rigorously) developed to better analyse and discuss our algorithm.
If you are interested in learning more about the technical details of our algorithm, please check out the resulting paper here. The paper was recently presented at AAAI-20’s special track on AI for Social Impact. We are also currently looking for partners with whom to run a pilot study. If that’s you, please reach out.
This post originally appeared on Sanket Shah’s blog and is cross-posted here with the author’s permission.
tags: AAAI, AAAI2020










