
ΑΙhub.org
Researchers use artificial intelligence to design supercompressible metamaterial
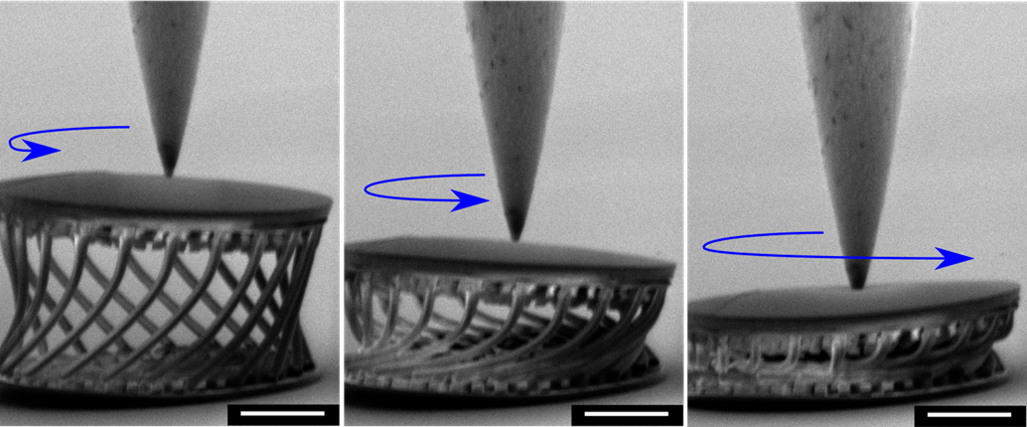
Researchers at TU Delft have developed a new material using Bayesian machine learning algorithms. Using the results of their computational simulations they have fabricated two designs at different length scales that transform polymers into supercompressible metamaterials.
Miguel Bessa, Assistant Professor in Materials Science and Engineering at TU Delft, got the inspiration for this research project during his time at the California Institute of Technology where, in a corner of the Space Structures Lab, he noticed a satellite structure that could open long solar sails from a very small package. He wondered if it would be possible to design a highly compressible, yet strong, material that could be compressed to a small fraction of its original volume.
In general, the next generation of materials needs to be adaptive, multi-purpose and tunable. This can be achieved by structure-dominated materials (metamaterials) that explore new geometries to achieve unprecedented properties and functionality. “However, metamaterial design has relied on extensive experimentation and a trial-and-error approach”, explains Bessa. “We argue in favour of inverting the process by using machine learning for exploring new design possibilities, while reducing experimentation to an absolute minimum.”
“We follow a computational data-driven approach for exploring a new metamaterial concept and adapting it to different target properties, choice of base materials, length-scales, and manufacturing processes.” Guided by machine learning, Bessa fabricated two designs at different length scales that transform brittle polymers into lightweight, recoverable and super-compressible metamaterials. The macro-scale design is tuned for maximum compressibility, while the micro-scale is designed for high strength and stiffness.
Machine learning offers scientists the opportunity to shift the design process from experimentally-guided investigations to computationally data-driven ones. Machine learning algorithms can find areas of the design space that people had never considered before. There is certainly much promise in this space, as Bessa concludes: “Data-driven science will revolutionize the way we reach new discoveries, and I can’t wait to see what the future will bring us.”
Read the research article in full
Bayesian Machine Learning in Metamaterial Design: Fragile Becomes Supercompressible
Miguel A. Bessa, Piotr Glowacki and Michael Houlder
Advanced Materials (2019)
The code behind the discovery
The team have made the code accessible to all, and you can check it out here.










