
ΑΙhub.org
Machine learning tool may help us better understand RNA viruses
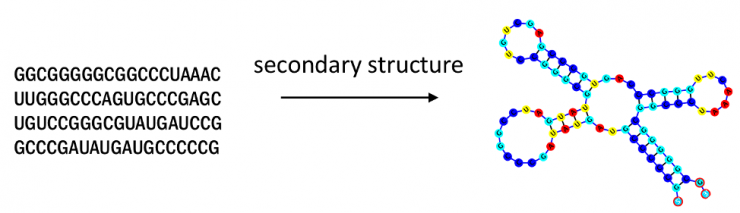
E2Efold is an end-to-end deep learning model developed at Georgia Tech that can predict RNA secondary structures, an important task used in virus analysis, drug design, and other public health applications.
Although the model has yet to be used in real-life applications, in research testing it has shown at least a 10 percent improvement in structure prediction accuracy compared to previous state-of-the-art methods according to Xinshi Chen, a Georgia Tech Ph.D. student specializing in machine learning and co-developer of the new tool.
“The model uses an unrolled algorithm for solving a constrained optimization as a component in the neural network architecture, so that it can directly incorporate a solution constraint, or prior knowledge, to predict the RNA base-pairing matrix,” said Chen.
E2Efold is not only more accurate, it is also considerably faster than current techniques.
Current methods are dynamic programming based, which is a much slower approach for predicting longer RNA sequences, such as the genomic RNA in a virus. E2Efold overcomes this drawback by using a gradient-based unrolled algorithm. It also takes advantage of graphic processing units to accelerate its computing process and is now the fastest method available.
RNA, or ribonucleic acid, is an essential building block that governs gene expression and is particularly important for RNA viruses, which consist only of RNA and the enwrapping virion proteins. These types of viruses make up a wide array of infectious diseases, including SARS, Dengue fever, the common cold, and others.
“Unlike most organisms, the genetic information of an RNA virus is RNA. As a result, almost every stage in the RNA virus life cycle relies on RNA heavily,” said Yu Li, a computational bioscience researcher from King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) and co-investigator.
“Take SARS, as an example. It belongs to an RNA virus. If we can predict its secondary and 3D structure accurately, based on its sequence information, we can potentially design drugs to bind to its local binding pocket and block the RNA from functioning. In other words, researchers might be able to develop treatments for the virus based on the specific local structure of the target RNA using this method as a starting point,” said Li.
One additional noteworthy ability of E2Efold is its ability to solve for pseudoknots. Pseudoknots are a biologically important RNA secondary structure that are present in roughly 40 percent of RNAs and assist with folding into 3D structures.
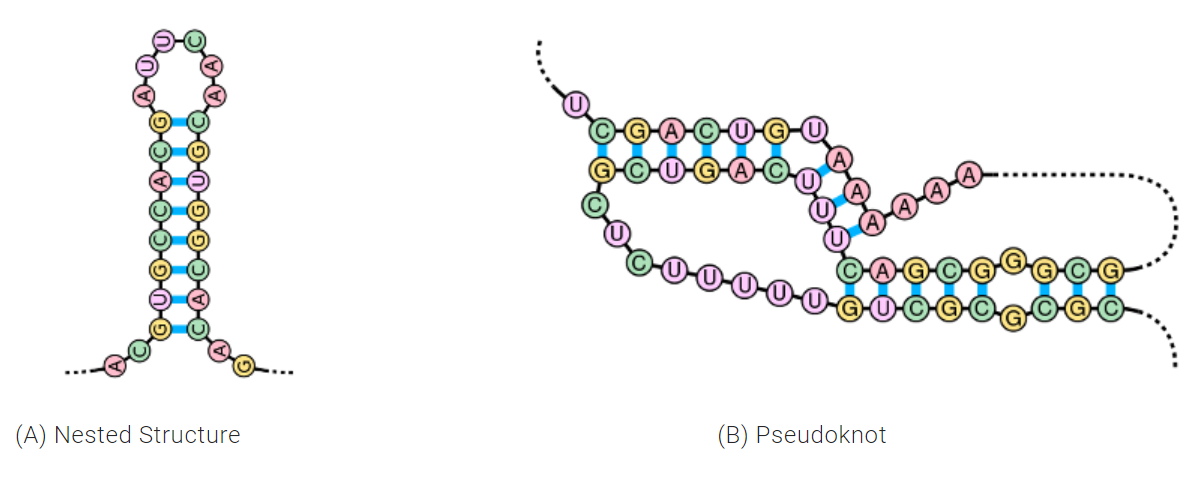
“Most previous models were restricted to only predict one type of RNA structure called nested structures. This excluded pseudoknots all together because they were computationally expensive,” said Chen. “In this paper, we predict RNA structures with pseudoknots by adopting a feed-forward model with a 25 percent greater accuracy than previous versions.”
Led by Georgia Tech School of Computational Science and Engineering (CSE) Associate Professor Le Song and KAUST Associate Professor Xin Gao, the team of researchers who created the model will present the paper outlining their findings at the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) 2020.
Although the focus of the paper is on RNA secondary prediction, E2Efold’s end-to-end deep learning approach is generic enough to also be applied to other problems such as protein folding and natural language understanding.









