
ΑΙhub.org
Learning to explore using active neural SLAM
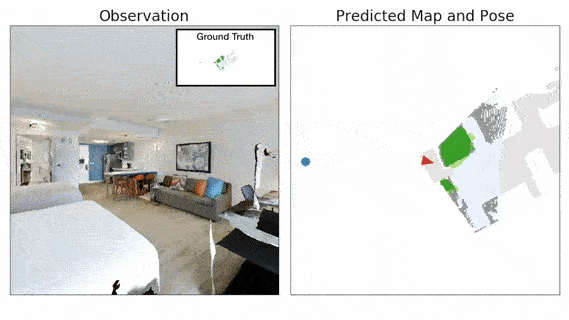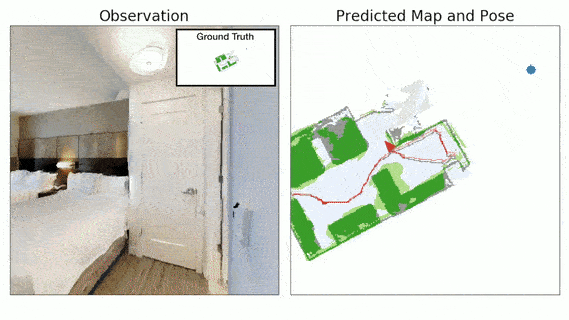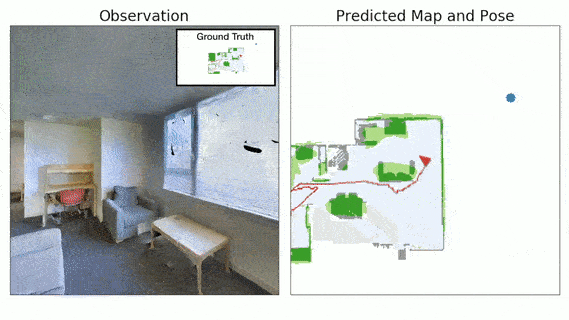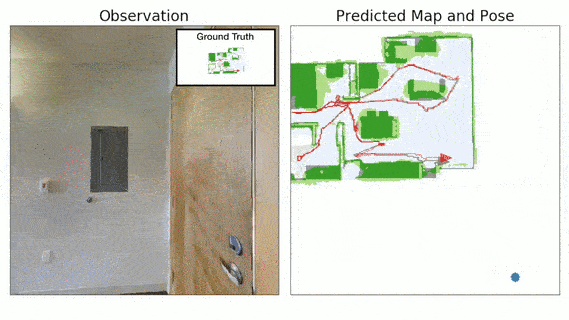
Advances in machine learning, computer vision and robotics have opened up avenues of building intelligent robots which can navigate in the physical world and perform complex tasks in our homes and offices. Exploration is a key challenge in building intelligent navigation agents. When an autonomous agent is dropped in an unseen environment, it needs to explore as much of the environment as fast as possible.

Exploring efficiently in a large environment requires the agent to know 3 things:
- where it has been before (i.e. Mapping)
- where it is now (i.e. Pose Estimation)
- where it needs to go (i.e. Planning)
How do we go about training autonomous exploration agents? One popular approach is using end-to-end deep Reinforcement Learning (RL). However, learning about mapping, pose estimation and planning implicitly in an end-to-end fashion is expensive and sample inefficient. This makes prior methods based on end-to-end RL ineffective at exploration in large environments.
In order to overcome these limitations, we present a modular system called Active Neural SLAM. It builds on ideas from Simultaneous Localization and Mapping literature in classical robotics and leverages learning for better performance and robustness. It uses structured spatial representations, hierarchical policies and analytical planners for learning to explore effectively in large scenes.
Active Neural SLAM
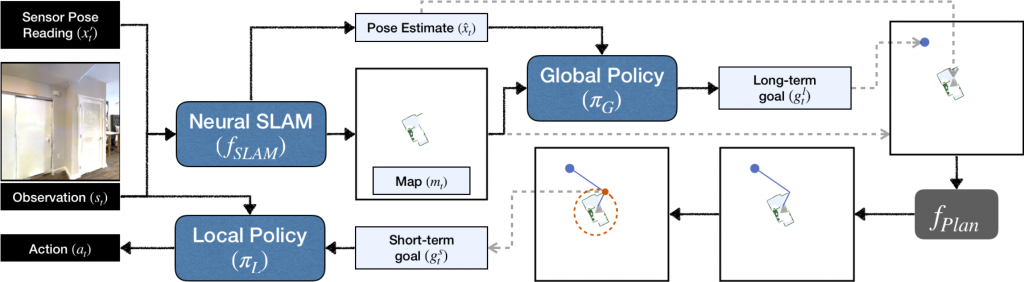
Active Neural SLAM (ANS) model consists of three components:
- Neural SLAM Module predicts the map of the environment and the agent pose based on the current observation and previous prediction:
- It uses convolutional operations to encode the visual observation followed by deconvolution operations to decode the map.
- It learns a structured map and pose representations.
- It is trained with supervised learning with binary cross-entropy loss for map prediction and mean-squared loss for pose prediction.
- Global Policy uses the predicted map and agent pose to produce a long-term goal which is converted to a short-term goal using analytical path-planning (like Dijkstra or A*) on the current map.
- It uses a CNN to produce a long-term goal.
- It operates at a course time-scale, once every 25 steps.
- It is trained using reinforcement learning with the increase in the explored area as the reward.
- Local Policy outputs navigational actions based on the current observation to reach the short-term goal.
- It uses a CNN + GRU.
- It operates at a fine time-scale, predicts a low-level navigation action every step, i.e., move-forward, turn-left or turn-right.
- It is trained using imitation learning with binary cross-entropy loss.
Results
We use the Habitat simulator with the Gibson and Matterport3D (MP3D) datasets for our experiments. In our exploration task setup, the objective to maximize the coverage in a fixed time budget of 1000 steps. Coverage is the total area in the map known to be traversable. We use two evaluation metrics, the absolute coverage area in ![]() (Cov) and the percentage of area explored in the scene (% Cov).
(Cov) and the percentage of area explored in the scene (% Cov).
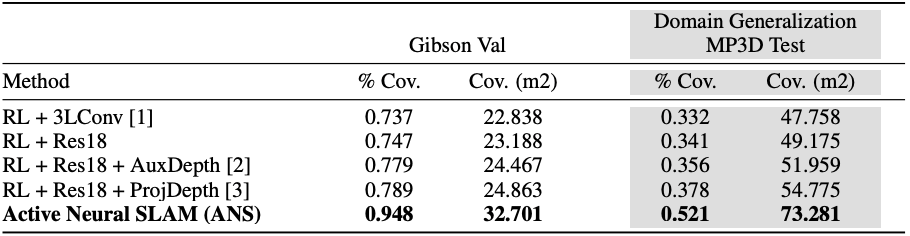
Baselines adapted from [1] Lample & Chaplot. AAAI-17, [2] Mirowski et al. ICLR-17, [3] Chen el al. ICLR-19.
We use 4 baselines based on end-to-end RL. All models are trained on Gibson training scenes and tested on (1) Gibson val set, and (2) MP3D test set (domain generalization). ANS outperforms baselines by a large margin on both test sets in terms of final coverage (see table above), and in terms of exploration efficiency (see plot below).
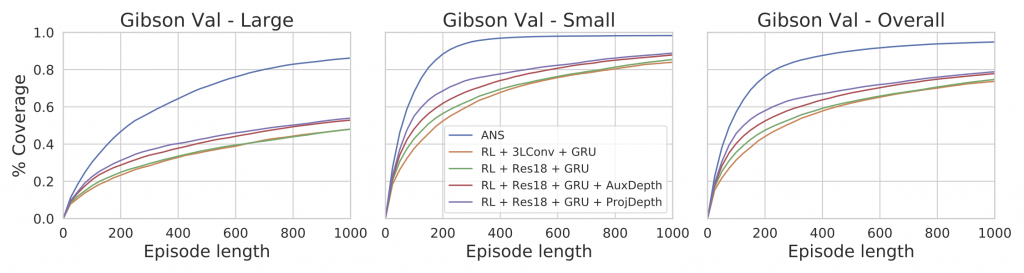
What makes Neural SLAM better?
- Inductive bias using Neural SLAM: Instead of letting the model figure out what is useful in the RGB observation for exploration, we tell it explicitly what to predict (i.e. map and pose). This leads to better generalization and sample efficiency.
- Reducing exploration search-space: The Global Policy operates at a course time-scale, picking a long-term goal every 25 steps. This reduces the time horizon for exploration, what needed 100 low-level navigation actions to be explored, can now be explored in 4 high-level actions.
- Path-Planning comes for free: End-to-end RL needs to learn path-planning implicitly, which is super data-intensive to learn. The Active Neural SLAM model does not need to learn planning. Because we use an explicit map representation, we can simply use classical planning algorithms.
PointGoal Task Transfer
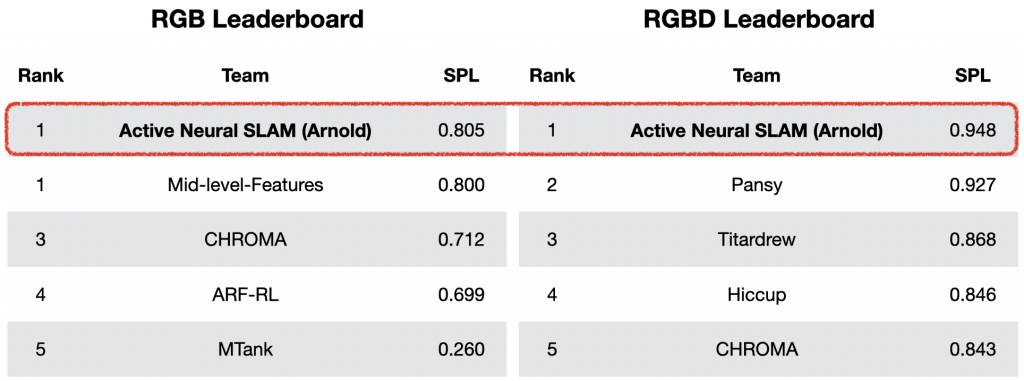
In the PointGoal task, the objective is to navigate to a goal location whose relative coordinates are given as input. The Active Neural SLAM model can be directly transferred to the PointGoal task without any additional training by just changing the Global policy to always output the PointGoal coordinates as the long-term goal. The ANS model trained for Exploration, when transferred to the PointGoal task can outperform all the baselines trained for the PointGoal Task by a large margin. It was the winner of the CVPR 2019 Habitat PointGoal Navigation Challenge.

Real-world Transfer
Our goal is to get these models to work not just in simulation but in the real-world. It is difficult to transfer navigation models to the real-world due visual and physical domain gap. While simulation environments based on real-world reconstructions close the visual domain gap, the perfect agent motion and pose sensor in the simulation were unrealistic.
In order to bridge this physical domain gap, we collect motion and sensor data in the real-world to create realistic noise models. We then train our exploration policy with noisy motion and pose sensors in the simulation using these noise models. Furthermore, due to the modularity, the pose estimation and global policy work directly on the map space, which is domain invariant. This allowed us to successfully transfer the trained Active Neural SLAM policy on the Locobot hardware platform using the PyRobot API.

Discussion and Next Steps
We presented a modular navigation system which leverages the strengths of both classical and learning-based methods. The use of learning provides flexibility with respect to input modalities (in the SLAM module), leverages structural regularities of the world (in global policies), and provides robustness to errors in state estimation (in local policies). It leads to significantly higher performance and up to 75 times better sample efficiency as compared to end-to-end reinforcement learning. Domain invariance of pose estimation & global policy, and realistic motion & sensor noise models allowed us to successfully transfer the model to the real-world. The Active Neural SLAM model can be further improved by incorporating explicit semantics and adding relocalization capabilities.
Incorporating Semantics: The current model only builds an obstacle map, without any explicit semantics. Incorporating semantics in the map and learning task-specific exploration are some challenges to tackle tasks such as Image Goal or Object Goal Navigation.
Relocalization: The current model can be coupled with prior relocalization techniques to add the ability to relocalize in a previously constructed map for more efficient navigation in known environments. Relocalization can also help in better pose estimation by mitigating pose drift.
Interested in more details?
Check out the links to the paper, complete codebase with pre-trained models, talk, slides and project webpage below.
Paper
Code
Talk
Slides
Webpage
This blog post was based on the following paper :
Devendra Singh Chaplot, Dhiraj Gandhi, Saurabh Gupta, Abhinav Gupta, and Ruslan Salakhutdinov. Learning To Explore Using Active Neural SLAM. In International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), 2020.
This article was initially published on the ML@CMU blog and appears here with the authors’ permission.









