
ΑΙhub.org
imodels: leveraging the unreasonable effectiveness of rules
imodels: A python package with cutting-edge techniques for concise, transparent, and accurate predictive modeling. All sklearn-compatible and easy to use.
By Chandan Singh, Keyan Nasseri and Bin Yu
Recent machine-learning advances have led to increasingly complex predictive models, often at the cost of interpretability. We often need interpretability, particularly in high-stakes applications such as medicine, biology, and political science (see here and here for an overview). Moreover, interpretable models help with all kinds of things, such as identifying errors, leveraging domain knowledge, and speeding up inference.
Despite new advances in formulating/fitting interpretable models, implementations are often difficult to find, use, and compare. imodels (github, paper) fills this gap by providing a simple unified interface and implementation for many state-of-the-art interpretable modeling techniques, particularly rule-based methods.
What’s new in interpretability?
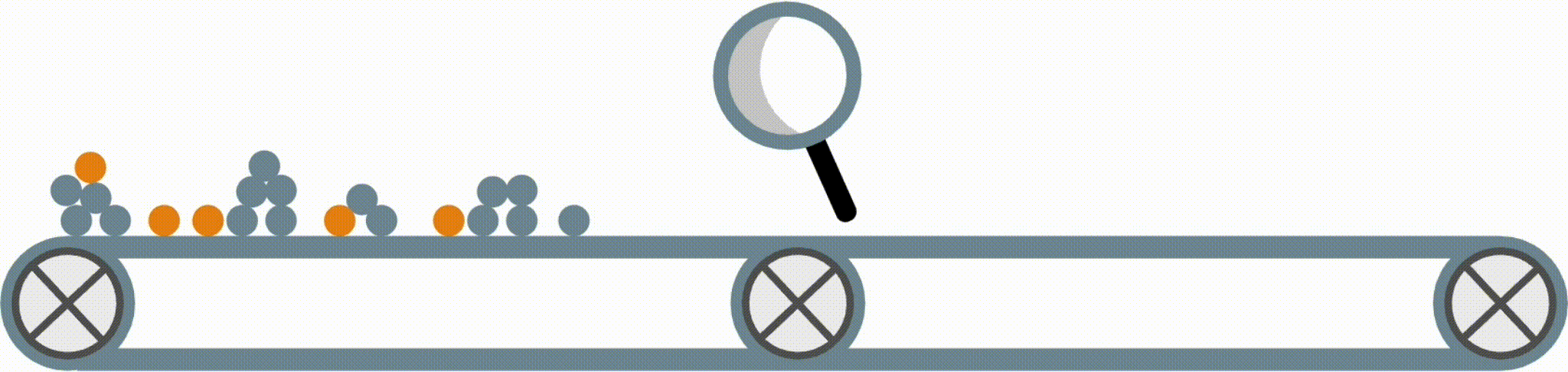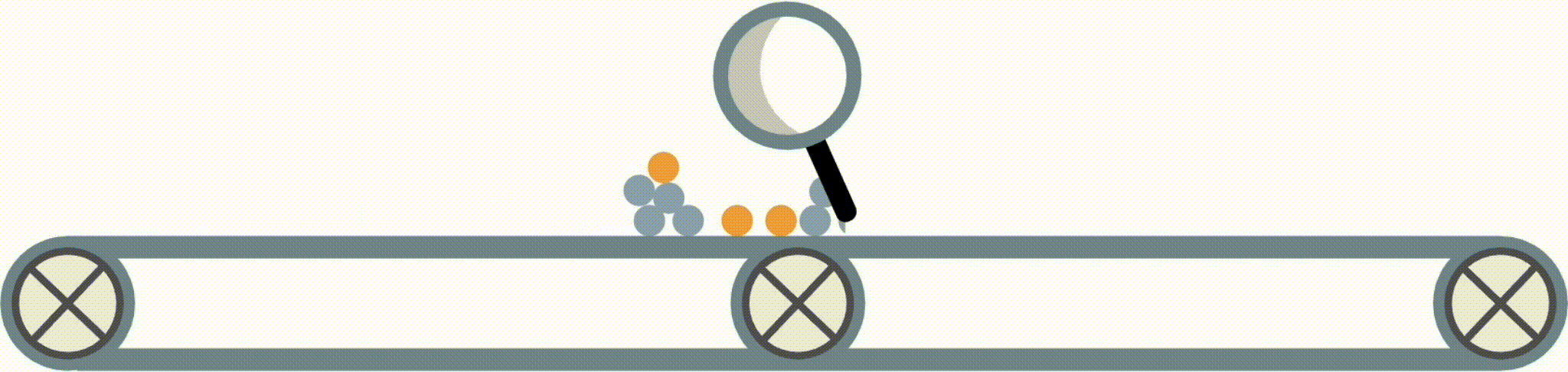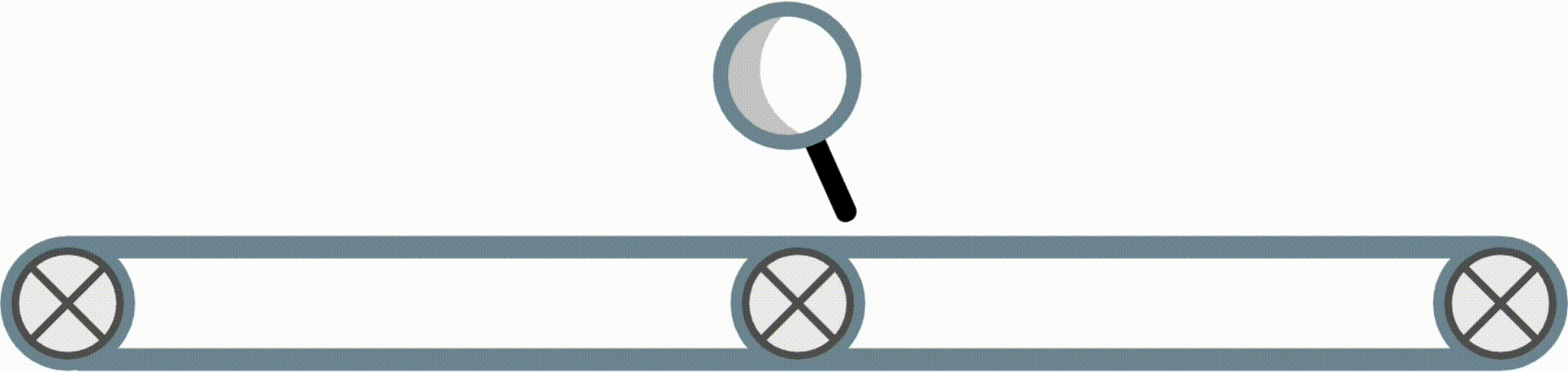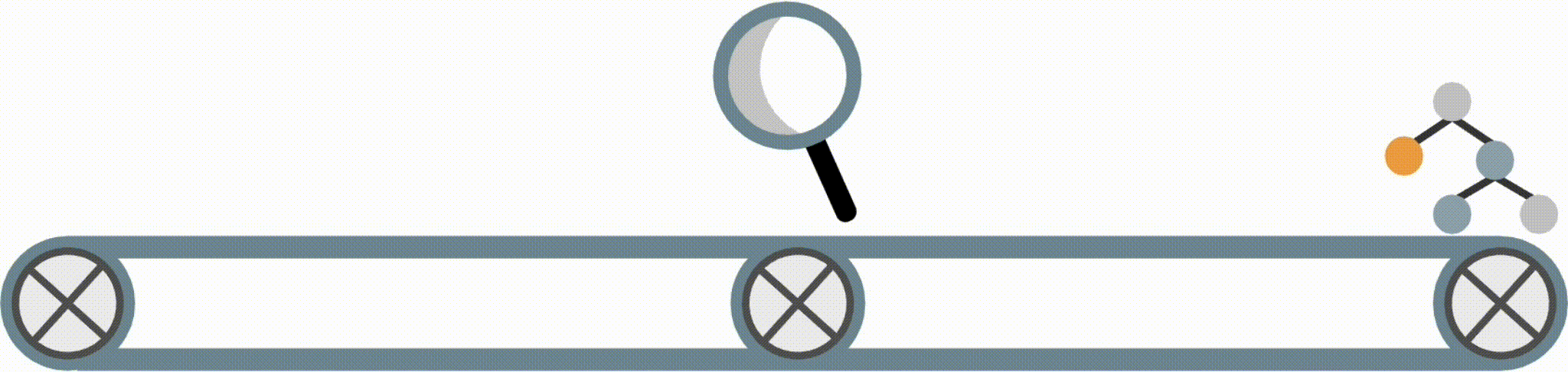
Interpretable models have some structure that allows them to be easily inspected and understood (this is different from post-hoc interpretation methods, which enable us to better understand a black-box model). Fig 1 shows four possible forms an interpretable model in the imodels package could take.
For each of these forms, there are different methods for fitting the model which prioritize different things. Greedy methods, such as CART prioritize efficiency, whereas global optimization methods can prioritize finding as small a model as possible. The imodels package contains implementations of various such methods, including RuleFit, Bayesian Rule Lists, FIGS, Optimal Rule Lists, and many more.

Fig 1. Examples of different supported model forms. The bottom of each box shows predictions of the corresponding model as a function of X1 and X2.
How can I use imodels?
Using imodels is extremely simple. It is easily installable (pip install imodels) and then can be used in the same way as standard scikit-learn models: simply import a classifier or regressor and use the fit and predict methods.
from imodels import BoostedRulesClassifier, BayesianRuleListClassifier,
GreedyRuleListClassifier, SkopeRulesClassifier # etc
from imodels import SLIMRegressor, RuleFitRegressor # etc.
model = BoostedRulesClassifier() # initialize a model
model.fit(X_train, y_train) # fit model
preds = model.predict(X_test) # discrete predictions: shape is (n_test, 1)
preds_proba = model.predict_proba(X_test) # predicted probabilities
print(model) # print the rule-based model
-----------------------------
# the model consists of the following 3 rules
# if X1 > 5: then 80.5% risk
# else if X2 > 5: then 40% risk
# else: 10% risk
An example of interpretable modeling
Here, we examine the Diabetes classification dataset, in which eight risk factors were collected and used to predict the onset of diabetes within 5 five years. Fitting, several models we find that with very few rules, the model can achieve excellent test performance.
For example, Fig 2 shows a model fitted using the FIGS algorithm which achieves a test-AUC of 0.820 despite being extremely simple. In this model, each feature contributes independently of the others, and the final risks from each of three key features is summed to get a risk for the onset of diabetes (higher is higher risk). As opposed to a black-box model, this model is easy to interpret, fast to compute with, and allows us to vet the features being used for decision-making.
Fig 2. Simple model learned by FIGS for diabetes risk prediction.
Conclusion
Overall, interpretable modeling offers an alternative to common black-box modeling, and in many cases can offer massive improvements in terms of efficiency and transparency without suffering from a loss in performance.
This post is based on the imodels package (github, paper), published in the Journal of Open Source Software, 2021. This is joint work with Tiffany Tang, Yan Shuo Tan, and amazing members of the open-source community.
This article was initially published on the BAIR blog, and appears here with the authors’ permission.
tags: deep dive










