
ΑΙhub.org
Art meets AI algorithms
By Eve Glasberg
Ali Hirsa, a professor in the Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research at Columbia Engineering, has always been interested in the possibility of merging art and technology. This curiosity led him to collaborate with New York-based artist Marco Gallotta on projects in which they could apply AI algorithms to works of art created by Gallotta.
Hirsa recently discussed this partnership with Columbia News, along with his career path from Wall Street to university professor, and advice for those contemplating a similar journey.
How did your collaboration with artist Marco Gallotta develop?
I have known Marco for eight years. I became familiar with his art during an auction at the primary school that our kids were attending. Marco heard about my research into AI applications in asset and wealth management, computational and quantitative finance, and algorithmic trading. One day I was describing some of the topics that I was teaching to graduate students at Columbia, and I mentioned that many of those machine learning and deep learning models and techniques can also be applied to other fields, such as replications of musical notes or the creation of images.
I soon learned that Marco had also been talking with Princeton Math Professor Gabriele Di Cerbo about art replication. I already knew Gabriele, and his research interest in algebraic geometry. In October 2019, the three of us teamed up to develop an AI tool to replicate Marco’s art.
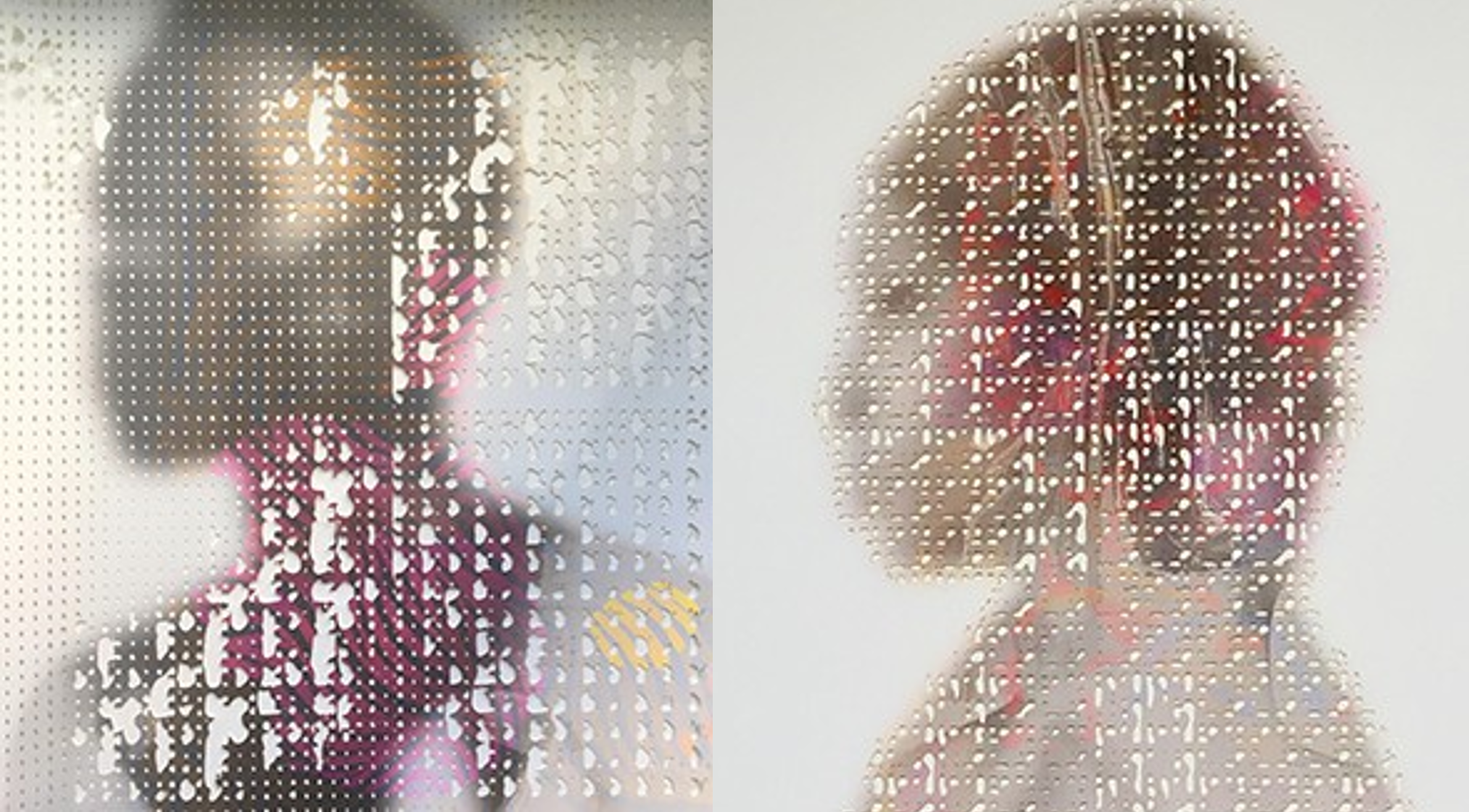
 “Adanna,” an AI portrait by Marco Gallotta.
“Adanna,” an AI portrait by Marco Gallotta.
Can you describe how AI is applied to the art?
In the project Art Meets AI, the focus has been on replication of images with connected components. What makes Marco’s art special is his paper-cutting technique, which is the result of constant research and experimentation. Paper-cutting is an ancient practice that Marco has made modern, giving it his vision by adding non-traditional elements such as acrylic colors and beeswax, and also through his choice of subjects.
He creates a new image from a source image by carefully cutting different parts of the original with distinct shapes. After taking those pieces out (either by hand or a laser machine), the newly created image has many holes of various, distinct shapes, but remains connected as one cohesive piece.
From the beginning, Gabriele and I knew that it would be challenging—and inspiring—to design an AI tool that would result in such cohesive works after the paper-cutting process. We developed a new algorithm, regularized generative adversarial network (regGAN), and trained it with images that had distinctive holes and patterns.
 “Eden,” an AI portrait by Marco Gallotta.
“Eden,” an AI portrait by Marco Gallotta.
Were you interested in applying AI to art before you met Marco?
Yes. I read a Christie’s article, Is Artificial Intelligence Set to Become Art’s Next Medium?, about a portrait of a man, Edmond Belamy, that was sold for $432,500 at the auction house in October of 2018. The portrait was not painted by a person; it was created by an algorithm, generative adversarial network (GAN). In the second major auction of AI art, at Sotheby’s in March of 2019, one of the works was a video installation that shows endless AI-generated portraits.
At the time, I added a few slides to my class lecture notes before going through the mathematical and algebraic formulas of the GAN. I was also then working with a few students on replicating classical musical notes (Mozart and Bach), and I thought we could apply some of those techniques in music to art.
After some more reading, I thought it would be interesting to see how GAN would work on Marco’s art, specifically his paper-cutting technique, and how he tries to preserve the image as one cohesive unit after removing pieces.
What goals can be achieved through this merging of art and technology?
The goal of developing an AI tool for art is to create images or portraits, not to replace artists. An artist like Marco can learn from images created by a machine. Marco has told us that as he observes images generated by AI, he gets inspired to create a new set of images, and by feeding his new images into the machine (or AI algorithm) to retrain it, the machine generates yet another set of images, as if they keep learning from each other. It’s important to note that AI cannot do anything without the artist’s images. Marco calls this process a 360-design collaboration, back and forth between machine and human.
 “Samantha,” an AI portrait by Marco Gallotta.
“Samantha,” an AI portrait by Marco Gallotta.
What was your career path to becoming an industrial engineer and a professor?
I started as a Wall Street quantitative analyst instead of going for a postdoc. Years later, I became a hedge fund manager, and utilized pattern recognition and statistical signal processing techniques for spotting mispricing and statistical arbitrage. I was always interested in teaching; I started tutoring at age 13, and taught through graduate school, in some cases as an extracurricular activity, simply because I enjoyed it.
From the beginning of my career, I liked to work with data, and I enjoy data mining. My PhD advisor always said, “let data do the talk, models are data-driven.” Throughout my industry years, prior to joining Columbia as a full-time professor, I worked on real applications of mathematical equations, and conducted research with academics in many disciplines. I love to bring industry and academia closer and narrow the gap.
Advice for anyone pursuing a career in engineering?
Always ask questions. Decision-making is data-driven, so work with data, and mine the data. If you are not a programmer, become one!









