
ΑΙhub.org
Using AlphaFold to find complex protein knots
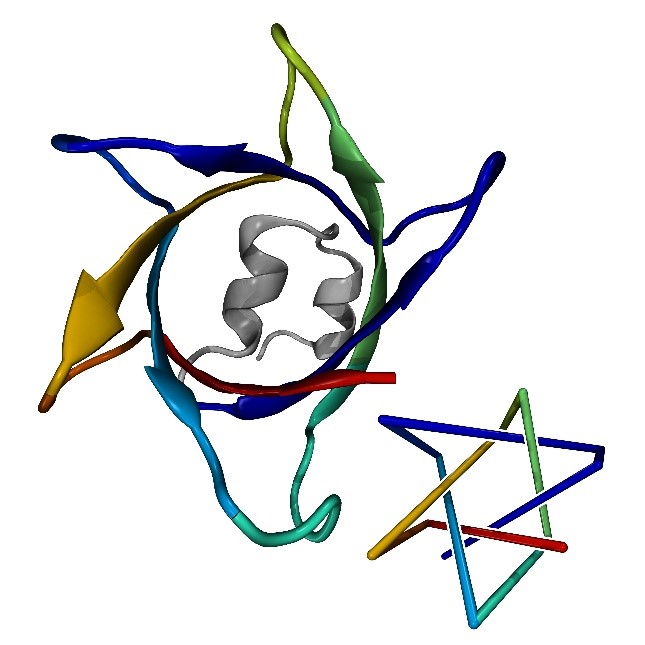 A complex protein knot with seven crossings (left) predicted by AlphaFold and a simplified representation (right). Image credit: Maarten Brems.
A complex protein knot with seven crossings (left) predicted by AlphaFold and a simplified representation (right). Image credit: Maarten Brems.
The question of how the chemical composition of a protein, the amino acid sequence, determines its 3D structure has been one of the biggest challenges in biophysics for more than half a century. This knowledge about the so-called “folding” of proteins is in great demand, as it contributes significantly to the understanding of various diseases and their treatment, among other things. For these reasons, Google’s DeepMind research team has developed AlphaFold, an artificial intelligence that predicts 3D structures.
A team consisting of researchers from Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) and the University of California, Los Angeles, has now taken a closer look at these structures and examined them with respect to knots. We know knots primarily from shoelaces and cables, but they also occur on the nanoscale in our cells. Knotted proteins can not only be used to assess the quality of structure predictions but also raise important questions about folding mechanisms and the evolution of proteins.
The most complex knots as a test for AlphaFold
“We investigated numerically all – that is some 100,000 – predictions of AlphaFold for new protein knots,” said Maarten A. Brems, a PhD student in the group of Dr Peter Virnau at Mainz University. The goal was to identify rare, high-quality structures containing complex and previously unknown protein knots to provide a basis for experimental verification of AlphaFold’s predictions. The study not only discovered the most complex knotted protein to date but also the first composite knots in proteins. The latter can be thought of as two separate knots on the same string. “These new discoveries also provide insight into the evolutionary mechanisms behind such rare proteins”, added Robert Runkel, a theoretical physicist also involved in the project. The results of this study were recently published in Protein Science.
Dr Peter Virnau is pleased with the results: “We have already established a collaboration with our colleague Dr Todd Yeates from UCLA to confirm these structures experimentally. This line of research will shape the biophysics community’s view of artificial intelligence – and we are fortunate to have an expert like Todd Yeates involved.”
Read the research paper
AlphaFold predicts the most complex protein knot and composite protein knots
Maarten A. Brems, Robert Runkel, Todd O. Yeates, Peter Virnau










