
ΑΙhub.org
Machine learning predicts heat capacities of metal-organic frameworks
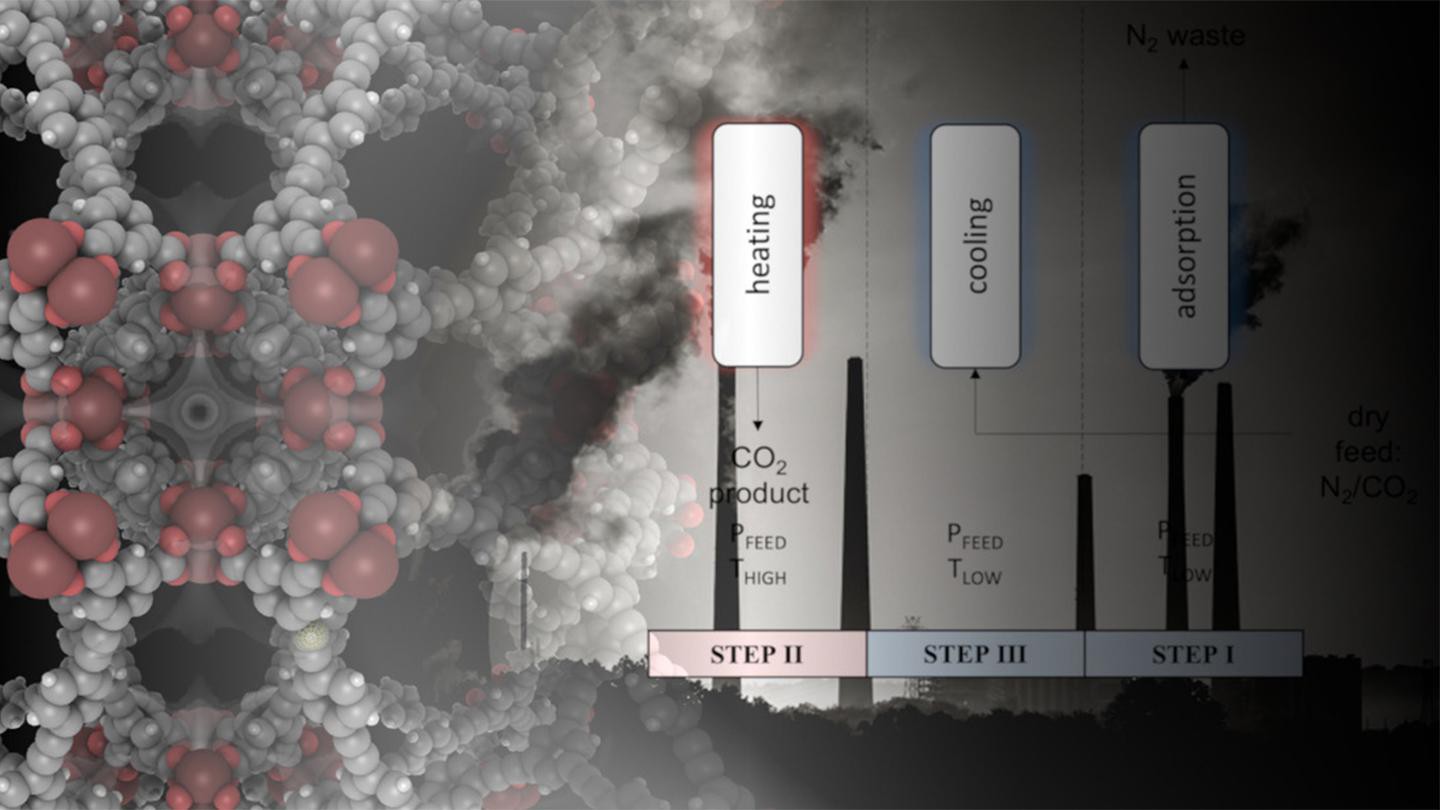 Metal organic frameworks capturing CO2 from flue gasses (Credit: S.M. Moosavi)
Metal organic frameworks capturing CO2 from flue gasses (Credit: S.M. Moosavi)
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are a class of materials that contain nano-sized pores. These pores give MOFs record-breaking internal surface areas, which make them extremely versatile for a number of applications: separating petrochemicals and gases, mimicking DNA, producing hydrogen, and removing heavy metals, fluoride anions, and even gold from water are just a few examples.
MOFs are the focus of Professor Berend Smit’s research at EPFL School of Basic Sciences, where his group employs machine learning in the discovery, design, and even categorization of the ever-increasing MOFs that currently flood chemical databases.
In a new study, Smit and his colleagues have developed a machine-learning model that predicts the heat capacity of MOFs. “This is about very classical thermodynamics,” says Smit. “How much energy is needed to heat up a material by one degree? Until now, all engineering calculations have assumed that all MOFs have the same heat capacity, for the simple reason that there is hardly any data available.” Seyed Mohamad Moosavi, a postdoc at Smit’s group, adds: “If there is no data, how can one make a machine-learning model? That looks impossible!”
The answer is the most innovative aspect of the work: a machine-learning model that predicts how the local chemical environment changes the vibrations of each atom in a MOF molecule. “These vibrations can be related to the heat capacity,” says Smit. “Before, a very expensive quantum calculation would give us a single heat capacity for a single material, but now we get up to 200 data points on these vibrations. So, by doing 200 expensive calculations, we had 40,000 data points to train the model on how these vibrations depend on their chemical environment.”
The researchers then tested their model against experimental data as a real-life check. “The results were surprisingly poor,” says Smit, “until we realized that those experiments had been done with MOFs that had solvent in their pores. So, we re-synthesized some MOFs and carefully removed the synthesis solvent –measured their heat capacity – and the results were in very good agreement with our model’s predictions!”
“Our research showcases how artificial intelligence (AI) can accelerate solving multi-scale problems,” says Moosavi. AI empowers us to think about our problems in a new way and even sometimes tackle them.”
To demonstrate the real-world impact of the work, engineers at Heriot-Watt University simulated the MOFs performance in a carbon capture plant. “We used quantum molecular simulations, machine learning, and chemical engineering in process simulations,” says Smit. “The results showed that with correct heat capacity values of MOFs the overall energy cost of the carbon capture process can be much lower than we originally assumed. Our work is a true multi-scale effort, with a huge impact on the techno-economic viability of currently considered solutions to tackle climate change.”
Other contributors: Freie Universität Berlin, University of Cambridge, Heriot-Watt University, and The University of Manchester.









