
ΑΙhub.org
Predicting properties of complex metamaterials
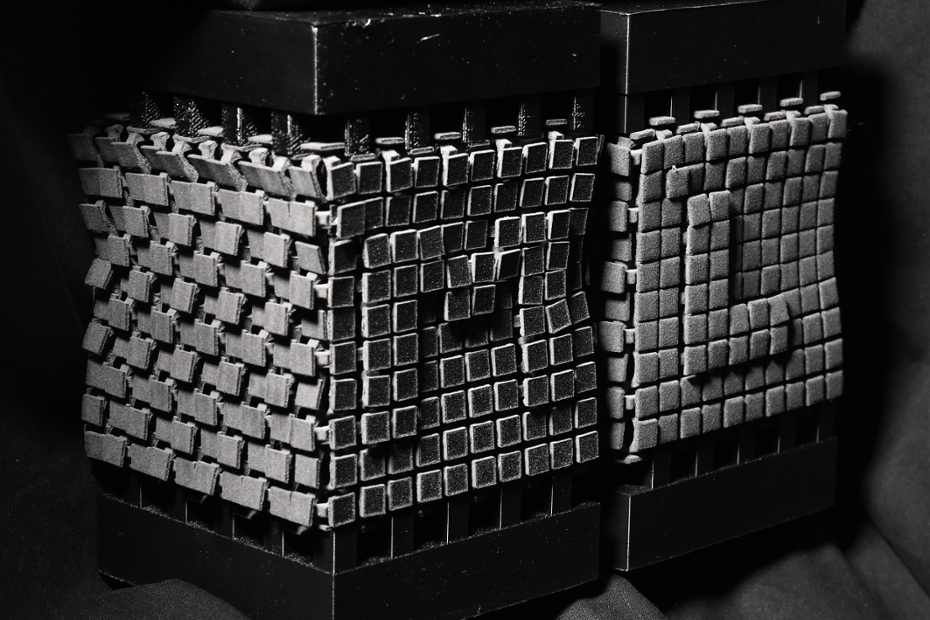 Two combinatorial mechanical metamaterials designed in such a way that the letters M and L bulge out in the front when being squeezed between two plates (top and bottom). Designing novel metamaterials such as this can be aided by machine learning. Image: Daan Haver and Yao Du.
Two combinatorial mechanical metamaterials designed in such a way that the letters M and L bulge out in the front when being squeezed between two plates (top and bottom). Designing novel metamaterials such as this can be aided by machine learning. Image: Daan Haver and Yao Du.
Given a 3D piece of origami, can you flatten it without damaging it? Just by looking at the design, the answer is hard to predict, because each and every fold in the design has to be compatible with flattening. This is an example of a combinatorial problem. New research led by the University of Amsterdam Institute of Physics and research institute AMOLF has demonstrated that machine learning algorithms can accurately and efficiently answer these kinds of questions. This is expected to give a boost to the artificial intelligence-assisted design of complex and functional (meta)materials.
Artificial materials
These are engineered materials whose properties are determined by their geometrical structure rather than their chemical composition. A piece of origami is also a type of metamaterial, whose ability to flatten (a physically well-defined property) is determined by how it is folded (its structure), rather than by the type of paper it is made of. More generally, smart design allows us to control precisely where or how a metamaterial will bend, buckle or bulge, which may be used for all sorts of things, from shock absorbers to unfolding solar panels on a satellite in space.
A typical combinatorial metamaterial studied in the lab is built up of two or more types or orientations of building blocks, which deform in distinct ways when a mechanical force is applied. If these building blocks are combined randomly, the material as a whole will usually not buckle under pressure because not all blocks will be able to deform the way they want to; they will jam. Where one building block wishes to bulge outward, its neighbour should be able to squish inward. For the metamaterial to easily buckle, all deformed building blocks need to fit together like a jigsaw puzzle. Just like changing a single fold can make a piece of origami unflattenable, changing a single block can make a “floppy” metamaterial rigid.
Hard to predict
While metamaterials have many potential applications, designing a new one is challenging. Starting with a particular set of building blocks, deducing the overall metamaterial properties for different structures often boils down to trial and error. In this day and age, we do not want to do all of this by hand. However, because the properties of combinatorial metamaterials are so sensitive to changes to individual building blocks, conventional statistical and numerical methods are slow and prone to mistakes.
Instead, the researchers found that machine learning may be the answer: even when given only a relatively small set of examples to learn from, convolutional neural networks are able to accurately predict the metamaterial properties of any configuration of building blocks down to the finest detail.
“This far exceeded our expectations,” says PhD student and first author Ryan van Mastrigt. “The accuracy of the predictions shows us that the neural networks have actually learned the mathematical rules underlying the metamaterial properties, even when we don’t know all the rules ourselves.”
This finding suggests that we can use AI to design new complex metamaterials with useful properties. More broadly, applying neural networks to combinatorial problems allows us to pose many exciting questions. Perhaps they can aid us in solving (combinatorial) problems in other contexts. And conversely, the findings can improve our understanding of neural networks themselves, by for instance demonstrating how the complexity of a neural network relates to the complexity of the problems it can solve.
Read the research in full
Machine Learning of Implicit Combinatorial Rules in Mechanical Metamaterials, Ryan van Mastrigt, Marjolein Dijkstra, Martin van Hecke, and Corentin Coulais.
Phys. Rev. Lett. 129 (2022)198003.









