
ΑΙhub.org
Learning to efficiently plan robust frictional multi-object grasps: interview with Wisdom Agboh

In their paper, Learning to Efficiently Plan Robust Frictional Multi-Object Grasps, Wisdom C. Agboh, Satvik Sharma, Kishore Srinivas, Mallika Parulekar, Gaurav Datta, Tianshuang Qiu, Jeffrey Ichnowski, Eugen Solowjow, Mehmet Dogar and Ken Goldberg trained a neural network to plan robust multi-object grasps. Wisdom summarises the key aspects of the work below:
What is the topic of the research in your paper?
When skilled waiters clear tables, they grasp multiple utensils and dishes in a single motion. On the other hand, robots in warehouses are inefficient and can only pick a single object at a time. This research leverages neural networks and fundamental robot grasping theorems to build an efficient robot system that grasps multiple objects at once.
Could you tell us about the implications of your research and why it is an interesting area for study?
To quickly deliver your online orders, amidst increasing demand and labour shortages, fast and efficient robot picking systems in warehouses have become indispensable. This research studies the fundamentals of multi-object robot grasping. It is easy for humans, yet extremely challenging for robots.
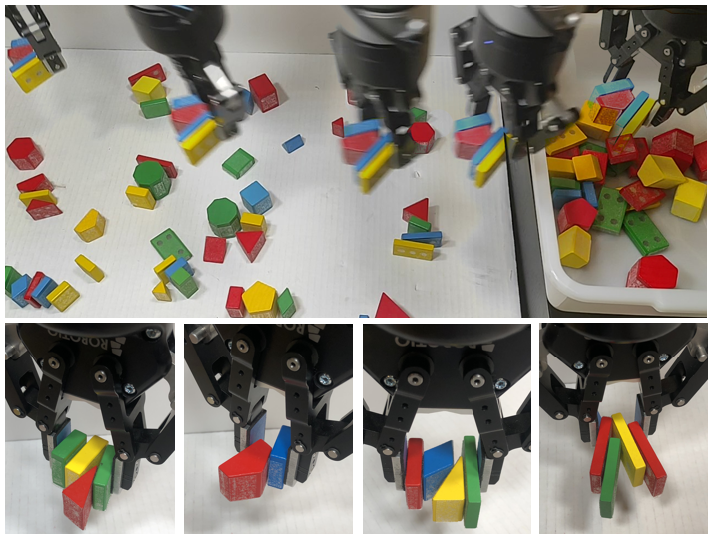 The decluttering problem (top) where objects must be transported to a packing box. Wisdom and colleagues found robust frictional multi-object grasps (bottom) to efficiently declutter the scene.
The decluttering problem (top) where objects must be transported to a packing box. Wisdom and colleagues found robust frictional multi-object grasps (bottom) to efficiently declutter the scene.
Could you explain your methodology?
We leverage a novel frictional multi-object grasping necessary condition to train MOG-Net, a neural network model using real examples. It predicts the number of objects grasped by a robot out of a target object group. We use MOG-Net in a novel robot grasp planner to quickly generate robust multi-object grasps.
In this video, you can see the robot grasping, using MOG-Net, in action.
What were your main findings?
In physical robot experiments, we found that MOG-Net is 220% faster and 16% more successful, compared to a single object picking system.
What further work are you planning in this area?
Can robots clear your breakfast table by grasping multiple dishes and utensils at once? Can they tidy your room floor by picking up multiple clothes at once? These are the exciting future research directions we will explore.
About Wisdom

|
Wisdom Agboh is a Research Fellow at the University of Leeds, and a Visiting Scholar at the University of California, Berkeley. He is an award-winning AI and robotics expert. |
Read the research in full
Learning to Efficiently Plan Robust Frictional Multi-Object Grasps
Wisdom C. Agboh, Satvik Sharma, Kishore Srinivas, Mallika Parulekar, Gaurav Datta, Tianshuang Qiu, Jeffrey Ichnowski, Eugen Solowjow, Mehmet Dogar and Ken Goldberg










