ΑΙhub.org
AI can track bees on camera. Here’s how that will help farmers

By Malika Nisal Ratnayake, Monash University; Adrian Dyer, Monash University, and Alan Dorin, Monash University
Artificial intelligence (AI) offers a new way to track the insect pollinators essential to farming.
In a new study, we installed miniature digital cameras and computers inside a greenhouse at a strawberry farm in Victoria, Australia, to track bees and other insects as they flew from plant to plant pollinating flowers.
Using custom AI software, we analysed several days’ video footage from our system to build a picture of pollination behaviour over a wide area.
In the same way that monitoring roads can help traffic run smoothly, our system promises to make pollination more efficient. This will enable better use of resources and increased food production.
A fresh set of eyes
With a growing human population and limited natural resources, food production needs to become more efficient and sustainable. Precision agriculture powered by new technologies, like AI, can help secure future food production.
Efficient pollination is crucial to produce healthy fruits, vegetables, legumes and nuts.
Optimal pollination requires just the right number of insect pollinator visits to flowers. Too few or too many visits, or visits by ineffective insect pollinators, can diminish the quality of food a flowering plant produces.
Typical techniques for monitoring insect pollination use direct visual observation or pan trapping, which are labour-intensive and take many days.
Additionally, without a very large number of trained observers it is impossible to collect simultaneous data across large farms. Yet such data are needed to provide time-critical evidence of the extent of crop pollination, before a season’s pollination window is closed.
With our digital system, however, a farm manager could obtain same-day data on crop pollination levels.
How fine-grained analysis of insect pollinator movement enables better food production
Tracking honeybees on strawberry plants
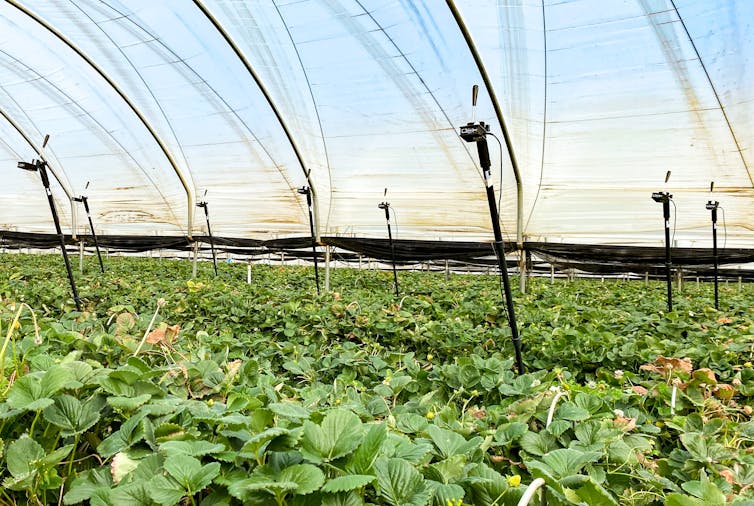
Our pollination monitoring system was set up at Sunny Ridge farm in a strawberry greenhouse open to insects. The array of cameras monitored insect activity among the strawberries, recording honeybees, hover flies, moths, butterflies and some wasps.
Video capture units placed over strawberry plants.
Managing big (insect) data with advanced software
The volume of data our system collects requires custom software to reliably track individual insects flying among complex foliage.
A key issue our software overcomes is identifying insect movements within a video sequence, so an individual insect on a single path isn’t accidentally counted multiple times. This enables accurate assessment of the number of insects in a region during a day, an analysis of their type (e.g. species), and monitoring of their flower visits.
Our custom software uses a hybrid detection model to detect and track insects and flowers in videos. This model combines the AI-based object-detection capabilities of deep learning using a convolutional neural network, together with separate foreground detection algorithms to identify the precise positions of insects and the flowers they visit in the recorded videos.
The software includes features to make data processing more efficient and save on computer power.
The insect paths our software produces are computed using a method called the Hungarian algorithm. This examines the positions of insects in each video frame in a sequence, and enables the identification of a match between the locations of the insects across a sequence of video frames.
By recording and visualising these paths, we gain an understanding of insect behaviour and the efficiency of pollination in a greenhouse.
Strawberries produce quality fruit after a minimum of four insect visits to an individual flower. Too many visits can actually damage flowers and reduce fruit quality.
Which insects drive pollination?
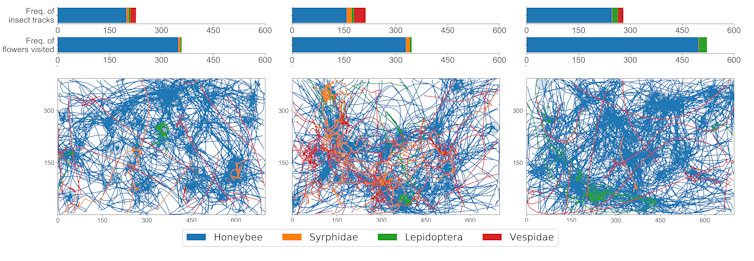
Insect counts, tracks and flower visits reported at three sample locations at our field site. Bar charts above the plots indicate the number of tracks and total number of flower visits for each insect type. Track colours represent different insect varieties. Flower locations are indicated by blue circles. Ratnayake et al., 2022.
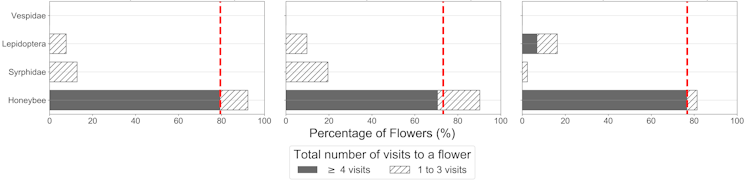
Honeybee flower visits were recorded more frequently in the monitored area than visits by other insects. Our analysis showed 68% of recorded flowers received the minimum number of four insect visits required for full fertilisation during the monitoring period.
While honeybees contributed the most to pollination, visits by other insects often resulted in individual flowers achieving the desired threshold of four visits, potentially improving the crop yield.
Contribution of different insect types towards strawberry pollination. Bar chart shows percentage of flowers visited by each insect type at three sample locations at our field site. The dark grey portion shows the percentage of flowers with over four (number of visits required for strawberry flower fertilisation) from each insect type. The red dashed line in the plots show the total percentage of flowers with more than four visits in a location. Ratnayake et al., 2022.
By detecting the numbers, types and timing of insects needed for optimal pollination, our monitoring system provides farmers the evidence they need to inform decision-making.
For example, knowing the extent to which a crop has been pollinated allows growers to alter hive locations and numbers to boost pollination shortfalls.
Farmers might also open or close greenhouse sidewalls to encourage or discourage insect visits from particular directions. They may decide to add attractant flowers to entice insects to explore crop regions that have been inadequately visited.
These simple interventions can ensure a higher rate of pollination success, and a higher yield of market-quality fruit. Smart insect management like this promises to help meet the need to feed a growing population with healthy produce.![]()
Malika Nisal Ratnayake, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Faculty of Information Technology, Monash University; Adrian Dyer, Associate Professor, Monash University, and Alan Dorin, Associate Professor, Faculty of Information Technology, Monash University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.