
ΑΙhub.org
Are model explanations useful in practice? Rethinking how to support human-ML interactions
Figure 1. This blog post discusses the effectiveness of black-box model explanations in aiding end users to make decisions. We observe that explanations do not in fact help with concrete applications such as fraud detection and paper matching for peer review. Our work further motivates novel directions for developing and evaluating tools to support human-ML interactions.
By Valerie Chen and Ameet Talwalkar
Model explanations have been touted as crucial information to facilitate human-ML interactions in many real-world applications where end users make decisions informed by ML predictions. For example, explanations are thought to assist model developers in identifying when models rely on spurious artifacts and to aid domain experts in determining whether to follow a model’s prediction. However, while numerous explainable AI (XAI) methods have been developed, XAI has yet to deliver on this promise. XAI methods are typically optimized for diverse but narrow technical objectives disconnected from their claimed use cases. To connect methods to concrete use cases, we argued in our Communications of ACM paper [1] for researchers to rigorously evaluate how well proposed methods can help real users in their real-world applications.
Towards bridging this gap, our group has since completed two collaborative projects where we worked with domain experts in e-commerce fraud detection and paper matching for peer review. Through these efforts, we’ve gleaned the following two insights:
- Existing XAI methods are not useful for decision-making. Presenting humans with popular, general-purpose XAI methods does not improve their performance on real-world use cases that motivated the development of these methods. Our negative findings align with those of contemporaneous works.
- Rigorous, real-world evaluation is important but hard. These findings were obtained through user studies that were time-consuming to conduct.
We believe that each of these insights motivates a corresponding research direction to support human-ML interactions better moving forward. First, beyond methods that attempt to explain the ML model itself, we should consider a wider range of approaches that present relevant task-specific information to human decision-makers; we refer to these approaches as human-centered ML (HCML) methods [10]. Second, we need to create new workflows to evaluate proposed HCML methods that are both low-cost and informative of real-world performance.
In this post, we first outline our workflow for evaluating XAI methods. We then describe how we instantiated this workflow in two domains: fraud detection and peer review paper matching. Finally, we describe the two aforementioned insights from these efforts; we hope these takeaways will motivate the community to rethink how HCML methods are developed and evaluated.
How do you rigorously evaluate explanation methods?
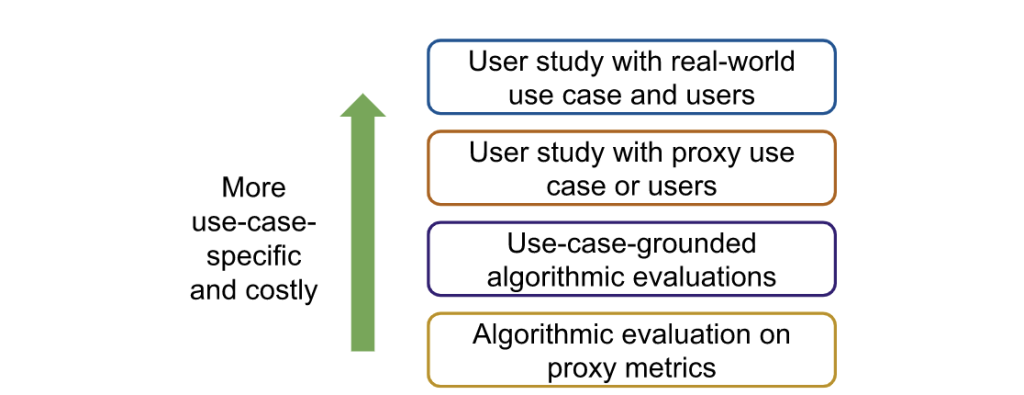
In our CACM paper [1], we introduced a use-case-grounded workflow to evaluate explanation methods in practice—this means showing that they are ‘useful,’ i.e., that they can actually improve human-ML interactions in the real-world applications that they are motivated by. This workflow contrasts with evaluation workflows of XAI methods in prior work, which relied on researcher-defined proxy metrics that may or may not be relevant to any downstream task. Our proposed three-step workflow is based on the general scientific method:
Step 1: Define a concrete use case. To do this, researchers may need to work closely with domain experts to define a task that reflects the practical use case of interest.
Step 2: Select explanation methods for evaluation. While selected methods might be comprised of popular XAI methods, the appropriate set of methods is to a large extent application-specific and should also include relevant non-explanation baselines.
Step 3: Evaluate explanation methods against baselines. While researchers should ultimately evaluate selected methods through a user study with real-world users, researchers may want to first conduct cheaper, noisier forms of evaluation to narrow down the set of methods in consideration (Figure 2).
Instantiating the workflow in practice
We collaborated with experts from two domains (fraud detection and peer review paper matching) to instantiate this use-case-grounded workflow and evaluate existing XAI methods:
Domain 1: Fraud detection [3]. We partnered with researchers at Feedzai, a financial start-up, to assess whether providing model explanations improved the ability of fraud analysts to detect fraudulent e-commerce transactions. Given that we had access to real-world data (i.e., historical e-commerce transactions for which we had ground truth answers of whether the transaction was fraudulent) and real users (i.e., fraud analysts), we directly conducted a user study in this context. An example of the interface shown to analysts is in Figure 3. We compared analysts’ average performance when shown different explanations to a baseline setting where they were only provided the model prediction. We ultimately found that none of the popular XAI methods we evaluated (LIME, SHAP, and Tree Interpreter) resulted in any improvement in the analysts’ decisions compared to the baseline setting (Figure 5, left). Evaluating these methods with real users additionally posed many logistical challenges because fraud analysts took time from their regular day-to-day work to periodically participate in our study.
Domain 2: Peer review paper matching [4]. We collaborated with Professor Nihar Shah (CMU), an expert in peer review, to investigate what information could help meta-reviewers of a conference better match submitted papers to suitable reviewers. Learning from our prior experience, we first conducted a user study using proxy tasks and users, which we worked with Professor Shah to design as shown in Figure 4. In this proxy setting, we found that providing explanations from popular XAI methods in fact led users to be more confident—-the majority of participants shown highlights from XAI methods believed the highlighted information was helpful—yet, they made statistically worse decisions (Figure 5 right)!
How can we better support human-ML interactions?
Through these collaborations, we identified two important directions for future work, which we describe in more detail along with our initial efforts in each direction.
We need to develop methods for specific use cases. Our results suggest that explanations from popular, general-purpose XAI methods can both hurt decision-making while making users overconfident. These findings have also been observed in multiple contemporaneous works (e.g., [7,8,9]). Researchers, instead, need to consider developing human-centered ML (HCML) methods [10] tailored for each downstream use case. HCML methods are any approach that provides information about the particular use case and context that can inform human decisions.
Our contributions: In the peer review matching setting, we proposed an HCML method designed in tandem with a domain expert [4]. Notably, our method is not a model explanation approach, as it highlights information in the input data, specifically sentences and phrases that are similar in the submitted paper and the reviewer profile. Figure 6 compares the text highlighted using our method to the text highlighted using existing methods. Our method outperformed both a baseline where there was no explanation and the model explanation condition (Figure 5, right). Based on these positive results, we plan to move evaluations of our proposed method to more realistic peer review settings. Further, we performed an exploratory study to better understand how people interact with information provided by HCML methods as a first step towards coming up with a more systematic approach to devise task-specific HCML methods [5].
We need more efficient evaluation pipelines. While user studies conducted in a real-world use case and with real users are the ideal way to evaluate HCML methods, it is a time- and resource-consuming process. We highlight the need for more cost-effective evaluations that can be utilized to narrow down candidate HCML methods and still implicate the downstream use case. One option is to work with domain experts to design a proxy task as we did in the peer review setting, but even these studies require careful consideration of the generalizability to the real-world use case.
Our contributions. We introduced an algorithmic-based evaluation called simulated user evaluation (SimEvals) [2]. Instead of conducting studies on proxy tasks, researchers can train SimEvals, which are ML models that serve as human proxies. SimEvals more faithfully reflects aspects of real-world evaluation because their training and evaluation data are instantiated on the same data and task considered in real-world studies. To train SimEvals, the researcher first needs to generate a dataset of observation-label pairs. The observation corresponds to the information that would be presented in a user study (and critically includes the HCML method), while the output is the ground truth label for the use case of interest. For example, in the fraud detection setting, the observation would consist of both the e-commerce transaction and ML model score shown in Figure 3(a) along with the explanation shown in Figure 3(b). The ground truth label is whether or not the transaction was fraudulent. SimEvals are trained to predict a label given an observation and their test set accuracies can be interpreted as a measure of whether the information contained in the observation is predictive for the use case.
We not only evaluated SimEvals on a variety of proxy tasks but also tested SimEvals in practice by working with Feedzai, where we found results that corroborate the negative findings from the user study [6]. Although SimEvals should not replace user studies because SimEvals are not designed to mimic human decision-making, these results suggest that SimEvals could be initially used to identify more promising explanations (Figure 6).
Conclusion
In summary, our recent efforts motivate two ways the community should rethink how to support human-ML interactions: (1) we need to replace general-purpose XAI techniques with HCML methods tailored to specific use cases, and (2) creating intermediate evaluation procedures that can help narrow down the HCML methods to evaluate in more costly settings.
For more information about the various papers mentioned in this blog post, see the links below:
[1] Chen, V., Li, J., Kim, J. S., Plumb, G., & Talwalkar, A. Interpretable Machine Learning. Communications of the ACM, 2022. (link)
[2] Chen, V., Johnson, N., Topin, N., Plumb, G., & Talwalkar, A. Use-case-grounded simulations for explanation evaluation. NeurIPS, 2022. (link)
[3] Amarasinghe, K., Rodolfa, K. T., Jesus, S., Chen, V., Balayan, V., Saleiro, P., Bizzaro, P., Talwalkar, A. & Ghani, R. (2022). On the Importance of Application-Grounded Experimental Design for Evaluating Explainable ML Methods. arXiv. (link)
[4] Kim, J. S., Chen, V., Pruthi, D., Shah, N., Talwalkar, A. Assisting Human Decisions in Document Matching. arXiv. (link)
[5] Chen, V., Liao, Q. V., Vaughan, J. W., & Bansal, G. (2023). Understanding the Role of Human Intuition on Reliance in Human-AI Decision-Making with Explanations. arXiv. (link)
[6] Martin, A., Chen, V., Jesus, S., Saleiro, P. A Case Study on Designing Evaluations of ML Explanations with Simulated User Studies. arXiv. (link)
[7] Bansal, G., Wu, T., Zhou, J., Fok, R., Nushi, B., Kamar, E., Ribeiro, M. T. & Weld, D. Does the whole exceed its parts? the effect of ai explanations on complementary team performance. CHI, 2021. (link)
[8] Adebayo, J., Muelly, M., Abelson, H., & Kim, B. Post hoc explanations may be ineffective for detecting unknown spurious correlation. ICLR, 2022. (link)
[9] Zhang, Y., Liao, Q. V., & Bellamy, R. K. Effect of confidence and explanation on accuracy and trust calibration in AI-assisted decision making. FAccT, 2020. (link)
[10] Chancellor, S. (2023). Toward Practices for Human-Centered Machine Learning. Communications of the ACM, 66(3), 78-85. (link)
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Kasun Amarasinghe, Jeremy Cohen, Nari Johnson, Joon Sik Kim, Q. Vera Liao, and Junhong Shen for helpful feedback and suggestions on earlier versions of the blog post. Thank you also to Emma Kallina for her help with designing the main figure!
This article was initially published on the ML@CMU blog and appears here with the authors’ permission.
tags: deep dive









