
ΑΙhub.org
PeSTo: an AI tool for predicting protein interactions
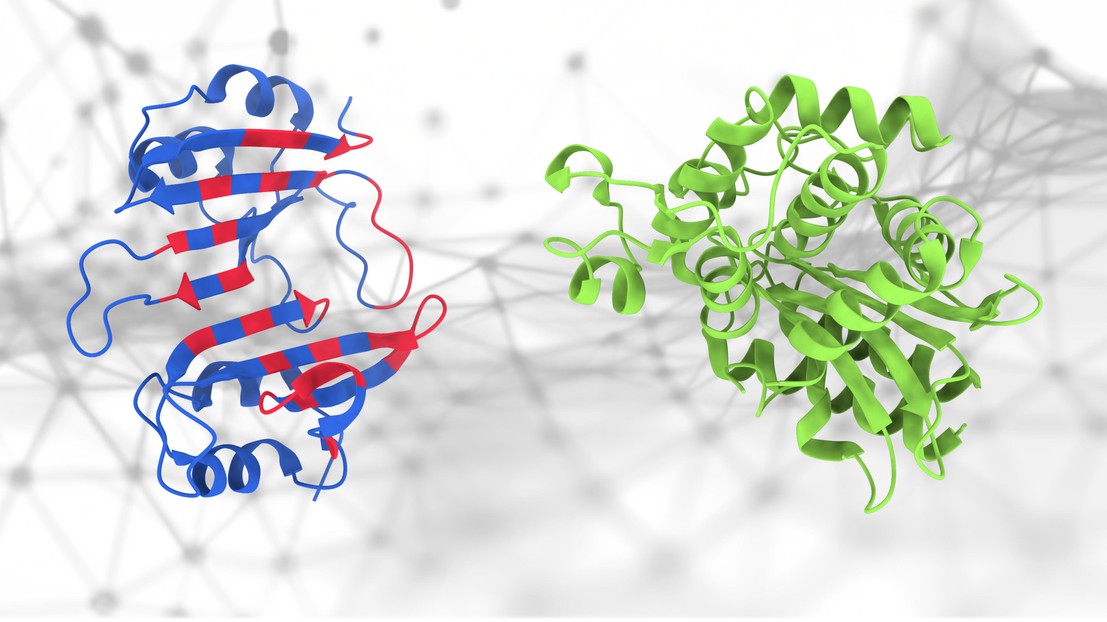 The geometric deep-learning method (PeSTo) used to predict protein binding interfaces. The amino acids involved in the protein binding interface are highlighted in red. Credit: Lucien Krapp (EPFL).
The geometric deep-learning method (PeSTo) used to predict protein binding interfaces. The amino acids involved in the protein binding interface are highlighted in red. Credit: Lucien Krapp (EPFL).
By Nik Papageorgiou
Proteins are essential to the biological functions of most living organisms. They have evolved to interact with other proteins, nucleic acids, lipids etc., and all of those interactions form large, “supra-molecular” complexes. This means that understanding protein interactions is crucial for understanding many cellular processes.
In a big step forward, scientists in the group of Matteo Dal Peraro at EPFL have developed a new tool called PeSTo (short for Protein Structure Transformer) that can predict the specific regions on the surface of a protein that can interact with other proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, ions, and small molecules. These interfaces are crucial for the formation of supramolecular complexes and function modulation.
PeSTo is built on a neural network based on transformer technology. In the context of machine learning, a transformer is a type of neural network designed to process sequential data, such as natural language by using self-attention mechanisms to weigh the importance of different parts of the input sequence and make predictions. Transformers are now at the core of many modern AI tools.
How does PeSTo work?
“The model evaluates the chemical and physical context of each atom by examining all nearby atoms,” says Lucien Krapp, the main developer of PeSTo. “Using the self-attention mechanism, it focuses on significant atoms and interactions within the protein structure. It means that this method effectively captures the complex interactions within protein structures to enable an accurate prediction of protein binding interfaces”.
Because PeSTo’s predictions are based solely on the position in space and the type of atoms, it can make predictions without needing to describe the physics and chemistry of the protein interface using additional external methods. This eliminates the ‘overhead’ of pre-computing molecular surfaces and additional properties, making it much faster, robust and more general than current methods.
It also means that PeSTo can run fast enough to process large volumes of protein structure data, e.g. ensembles from molecular dynamics simulations or entire foldomes. Ultimately, this enables faster discovery of interfaces that go unseen in conventional static structures resolved experimentally.
PeSTo outperforms other methods for predicting protein interaction interfaces and can predict interactions with nucleic acids, lipids, ligands, ions, and small molecules with high confidence. The model’s low computational cost makes it a valuable tool for the scientific community.
PeSTo applied to the human foldome
The researchers unleashed PeSTo on the human foldome, a growing database of predicted protein structures. They analyzed the interactions that human proteins have with other molecules, and produced detailed information about the human “interfaceome” – the sum total of all protein interacting interfaces in the human body. To do this, the researchers used the AlphaFold European Bioinformatics Institute (AF-EBI) database.
The researchers have made PeSTo available in a user-friendly web server, free of charge and prior registration. The server can take any protein structure in PDB format. The predicted interfaces can be visualized directly in the browser with additional information on the confidence of the prediction on a per-residue basis.
Publishing in Nature Communications, the scientists highlight numerous advantages of PeSTo over older methods, particularly that it can work with all kinds of molecules without needing to know all the details about their chemistry and physics. This makes PeSTo a more flexible, powerful and general tool for studying molecular systems and their interactions.
Read the research in full
PeSTo: parameter-free geometric deep learning for accurate prediction of protein binding interfaces, Lucien F. Krapp, Luciano A. Abriata, Fabio Cortés Rodriguez, Matteo Dal Peraro, Nature Communications (2023).









