
ΑΙhub.org
RoboChem: a platform for optimising photochemical processes
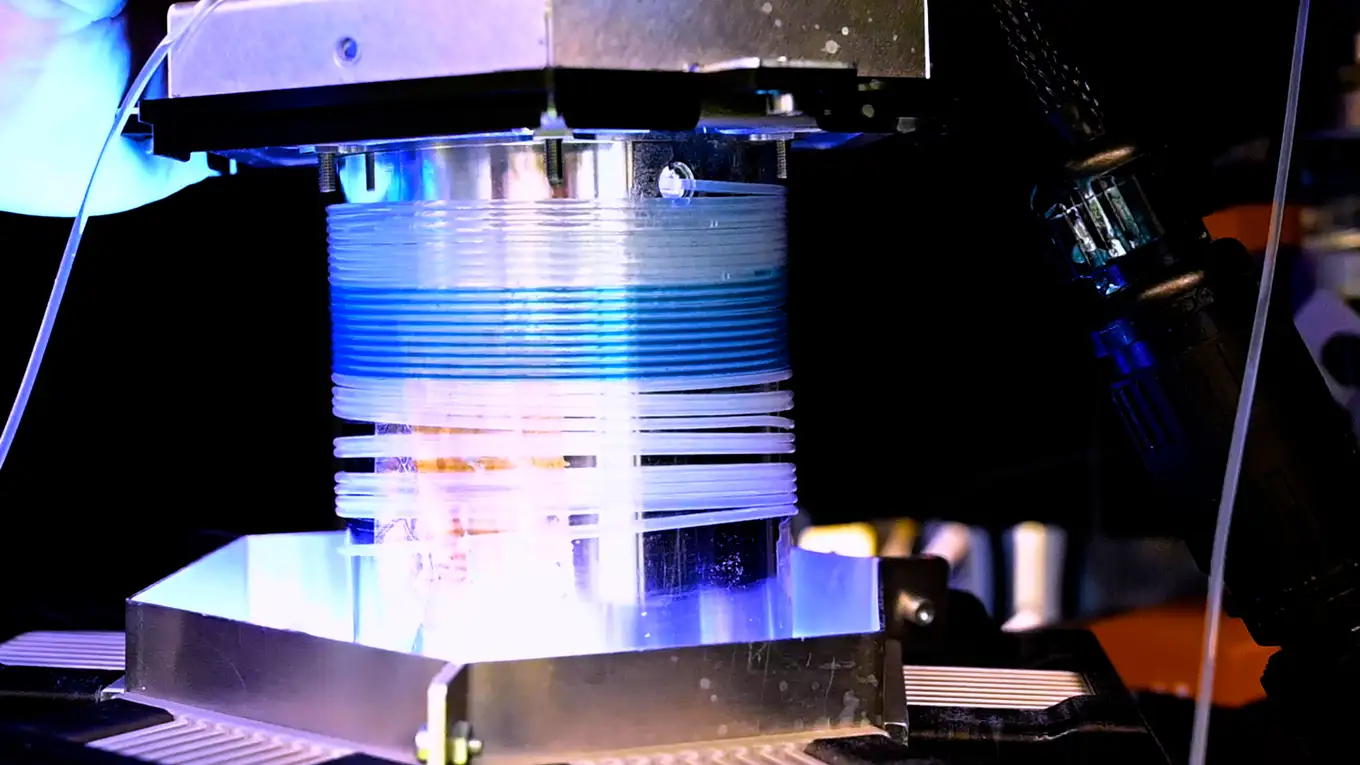 RoboChem explores chemical reactions in a flow system that includes a LED-powered photochemical reactor. Image credit: UvA/HIMS.
RoboChem explores chemical reactions in a flow system that includes a LED-powered photochemical reactor. Image credit: UvA/HIMS.
Chemists of the University of Amsterdam (UvA) have developed an autonomous chemical synthesis robot with an integrated machine learning unit. Dubbed “RoboChem”, the benchtop device combines software and hardware that iteratively determines optimal, substrate-specific conditions for photochemical processes in a scalable, flow-based architecture. RoboChem’s first results were published on 25 January in the journal Science.
RoboChem was developed by the group of Professor Timothy Noël at the UvA’s Van ‘t Hoff Institute for Molecular Sciences. Their paper shows that RoboChem can perform a variety of reactions while producing minimal amounts of waste. Noël: “In a week, we can optimise the synthesis of about ten to twenty molecules. This would take a PhD student several months.” The robot not only yields the best reaction conditions, but also provides the settings for scale-up. “This means we can produce quantities that are directly relevant for suppliers to the pharmaceutical industry, for example.”
The expertise of the Noël group is in flow chemistry, a novel way of performing chemistry where a system of small, flexible tubes replaces beakers, flasks and other traditional chemistry tools. In RoboChem, a robotic needle carefully collects starting materials and mixes these together in small volumes of just over half a millilitre. These then flow through the tubing system towards the reactor. There, the light from powerful LEDs triggers the molecular conversion by activating a photocatalyst included in the reaction mixture. The flow then continues towards an automated NMR spectrometer that identifies the transformed molecules. These data are fed back in real-time to the computer that controls RoboChem. “This is the brain behind RoboChem,” says Noël. “It processes the information using artificial intelligence. We use a machine learning algorithm that autonomously determines which reactions to perform. It always aims for the optimal outcome and constantly refines its understanding of the chemistry.”
Watch the video where Timothy Noël and first author Aidan Slattery explain RoboChem and it’s relevance to chemical discovery.
The group put a lot of effort into substantiating RoboChem’s results. All of the molecules now included in the Science paper were isolated and checked manually. Noël says the system has impressed him with its ingenuity: “I have been working on photocatalysis for more than a decade now. Still, RoboChem has shown results that I would not have been able to predict. For instance, it has identified reactions that require only very little light. At times I had to scratch my head to fathom what it had done. You then wonder: would we have done it the same way? In retrospect, you see RoboChem’s logic. But I doubt if we would have obtained the same results ourselves. Or not as quickly, at least.”
The researchers also used RoboChem to replicate previous research published in four randomly selected papers. They then determined whether Robochem produced the same – or better – results. “In about 80% of the cases, the system produced better yields. For the other 20%, the results were similar,” Noël says. “This leaves me with no doubt that an AI-assisted approach will be beneficial to chemical discovery in the broadest possible sense.”
Breakthroughs in chemistry using AI
According to Noël, the relevance of RoboChem and other “computerised” chemistry also lies in the generation of high-quality data, which will benefit the future use of AI. “In traditional chemical discovery only a few molecules are thoroughly researched. Results are then extrapolated to seemingly similar molecules. RoboChem produces a complete and comprehensive dataset where all relevant parameters are obtained for each individual molecule. That provides much more insight.”
Another feature is that the system also records “negative” data. In current scientific practice, most published data only reflects successful experiments. “A failed experiment also provides relevant data,” says Noël. “But this can only be found in the researchers’ handwritten lab notes. These are not published and thus unavailable for AI-powered chemistry. RoboChem will change that, too. I have no doubt that if you want to make breakthroughs in chemistry with AI, you will need these kinds of robots.”
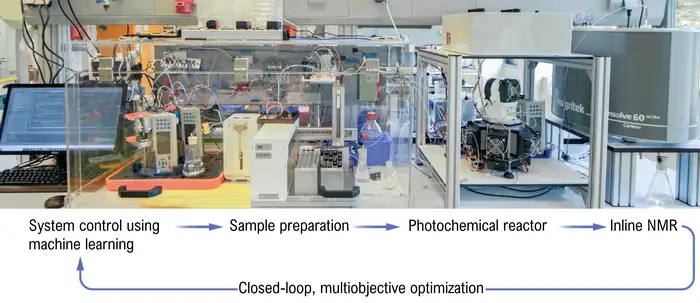 Overview of the RoboChem system and its main components. Image: UvA/HIMS.
Overview of the RoboChem system and its main components. Image: UvA/HIMS.
Find out more
- The paper: Automated self-optimization, intensification, and scale-up of photocatalysis in flow, Aidan Slattery, Zhenghui Wen, Pauline Tenblad, Jesús Sanjosé-Orduna, Diego Pintossi, Tim den Hartog, Timothy Noel, Science (2024).
- The story behind the Science paper: How our team created RoboChem
- Research group Flow Chemistry
- Van ‘t Hoff Institute for Molecular Sciences









