
ΑΙhub.org
From sketches to a robot with artificial intelligence
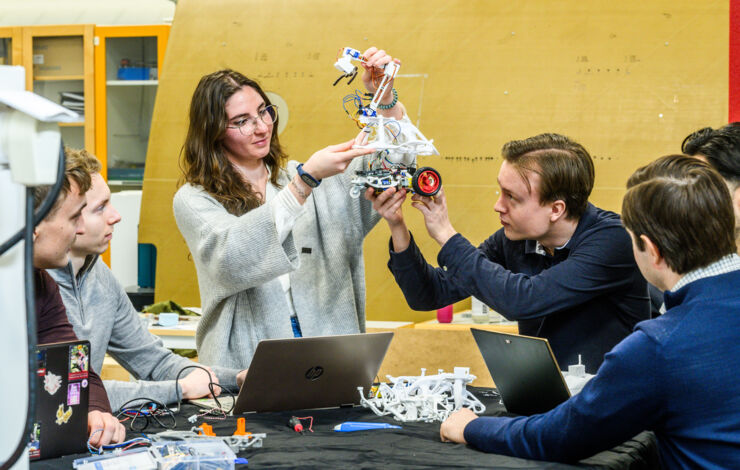 PhD-student Elena Jiménez Romanillo with the Master´s students working on a robot with assistance from generative AI. Photo credit: Thor Balkhed.
PhD-student Elena Jiménez Romanillo with the Master´s students working on a robot with assistance from generative AI. Photo credit: Thor Balkhed.
By Ulrik Svedin
How do you develop a product with as little human involvement as possible? Linköping University students built a robot using generative artificial intelligence.
From an initial idea with AI-generated images to the final stages of optimisation, generative AI (GAI) supported the students throughout the design process.
“I mainly used ChatGPT to program the robot’s navigation and control,” says Arad Jafari, master’s student in technical design.
Programming
The robot is similar to a radio-controlled car, with a small arm and a grapple claw in the front. With the sensors, it is able to drive along a lined path and stop in the designated place, pick up a small box and transport it further.

Master’s student Arad Jafari. Photo credit: Thor Balkhed.
“I’ve always been interested in programming, but my knowledge has been limited. Both my interest and my skills have increased with this project. Robotics and coding were new to me. In addition to the help I have received from the AI, ChatGPT has also acted as a digital mentor,” says Arad Jafari.
How did that work in practice?
“For instance, we received AI support with brainstorming and various solutions to the requirements we have on the robot. What electronic components are needed? How do the components work and how should they be connected? Here, ChatGPT has helped generate all the code for the different solutions.”
The task they faced on the course ‘Design and production’ was to develop a so-called proof of concept, i.e. to prove that something is feasible, in this case by designing, constructing and programming using generative AI – and without too much prior knowledge.
The students´ curiosity
The students were supported by a doctoral student and an external supervisor from the forklift manufacturer Toyota Material Handling. Their supervisor Tomas Jankauskas, senior designer, explains why the industry needs to cooperate with LiU: “We risk turning into dinosaurs if we don’t take advantage of the students’ curiosity. They represent the future. I’ve given them a framework and provided advice, but the students have been the driving force in this project,” he says.
By asking questions to the Open AI tools and a number of other tools (such as ChatGPT, Vizcom and others), they have designed a vehicle with an open chassis in futuristic style. With the help of AI, they have also received assembly instructions. To attach the chassis, they had to make small adjustments manually. But they have basically gone from AI-generated images and 3D models on the screen to 3D printing on the spot. It was difficult in the beginning.
Challenges
“There were products that had three wheels on one side and two wheels on the other. Or an arm that didn’t reach over the hood. A lot that didn’t work. The advantage is that it’s a quick process, so you can fail several times. The difficulty lies in deciding what to move forward with,” says Vivaldus Berglund.
Do you have any tips on how to write questions to an AI?
“We saw that you can ask the AI how best to type a prompt to achieve a certain result. This made the final prompt much better. Another tip is to be specific. The AI will look up shapes based on what it thinks we mean,” says Ville Jonsson.
Why is it important to try to get AI to do the whole job?
“Drawing and programming takes time and costs money. If a manufacturer discovers that it’s possible to automate, that’s of course interesting,” says Johan Asp.
But doctoral student Elena Jiménez Romanillos objects:
“You need to monitor the whole process very carefully and reflect. You have to understand what is happening all the time and spot the mistakes. Otherwise, you’ll lose all the efficiency improvements that can occur with AI,” she says.

PhD-student Elena Jiménez Romanillos. Photo credit: Thor Balkhed
“It’s about how you take facts into account, see connections, draw your own conclusions, evaluate and finally produce and create something new” says Elena Jiménez Romanillos. “For example, the use of AI varies depending on the students’ prior knowledge,”
“Artificial intelligence in the learning process is still a new thing. It’s interesting to see how students search for information and discover completely new tools, almost day by day,” says Torbjörn Andersson.
Exhibition
The students and teachers participated in Milan Design week, 15–21 April 2024, together with Toyota’s exhibitors. They promoted the MSc Programme in Design and Product Development, and shared their experiences of programming and designing using generative artificial intelligence.









