
ΑΙhub.org
Preparing for emergency response with partial network information
By Kristen Perez, Machine Learning Center at Georgia Tech and School of Computational Science and Engineering.
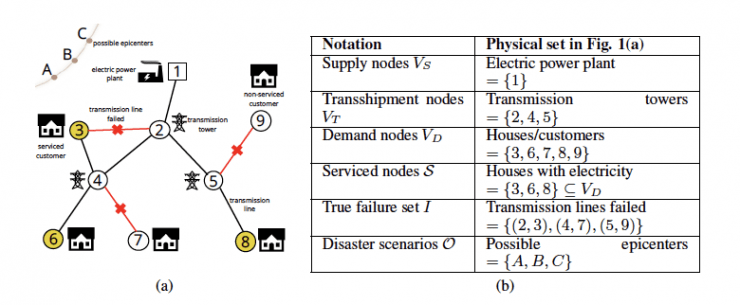
Natural disasters cause considerable economic damage, loss of life, and network disruptions each year. As emergency response and infrastructure systems are interdependent and interconnected, quick assessment and repair in the event of disruption is critical.
School of Computational Science and Engineering (CSE) Associate Professor B. Aditya Prakash is leading a collaborative effort with researchers from Georgia Institute of Technology, University of Oklahoma, University of Iowa, and University of Virginia to determine the state of an infrastructure network during such a disruption. Prakash’s group has also been collaborating closely with the Oak Ridge National Laboratory on such problems in critical infrastructure networks.
However, according to Prakash, quickly determining which infrastructure components are damaged in the event of a disaster is not easily done after a disruption.
“If there is a disruption caused by an earthquake or hurricane and some things go down in the power grid, critical infrastructure system, transportation network, or the energy distribution network, how do you figure out what things have failed?” asked Prakash.
“The big problem in figuring out what has gone wrong is that all of these networks are highly decentralized and spread out. Usually there will be no central command or ‘oracle’ that immediately knows perfectly what is out, what is on, what is fine, and what is not.”
Given these networks’ decentralized organization and sparse installation of real-time monitoring systems, only a partial observation of the network is typically available after a disaster.
By using connectivity queries to map network states, Prakash’s team outlines in their recent paper how to determine the damage of an entire network from the portion of observable and operational nodes.
The team aims to infer failed network components by examining two-node characteristics: The partial information available from reachable nodes and a small sample of point probes which are typically more practical to obtain in a failure.
Modeling their research on real utility network data gathered by the University of Oklahoma, Prakash’s team proposes using an information-theoretic formulation called the minimum description length (MDL) principle. This is the notion that the best way to describe any data is the shortest one. Hence the researchers try to find those failed components, particularly the critical ones affecting overall system performance, which contain enough information to effectively minimize the MDL cost.
Alexander Rodriguez, a CSE Ph.D. student and lead author, presented the findings of this research this week at the 2020 Neural Processing and Information Systems (NeurIPS) conference as part of the Workshop on Artificial Intelligence for Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Response.
tags: NeurIPS, NeurIPS2020








