
ΑΙhub.org
Physically realistic attacks on deep reinforcement learning

By Adam Gleave
Deep reinforcement learning (RL) has achieved superhuman performance in problems ranging from data center cooling to video games. RL policies may soon be widely deployed, with research underway in autonomous driving, negotiation and automated trading. Many potential applications are safety-critical: automated trading failures caused Knight Capital to lose USD 460M, while faulty autonomous vehicles have resulted in loss of life.
Consequently, it is critical that RL policies are robust: both to naturally occurring distribution shift, and to malicious attacks by adversaries. Unfortunately, we find that RL policies which perform at a high-level in normal situations can harbor serious vulnerabilities which can be exploited by an adversary.
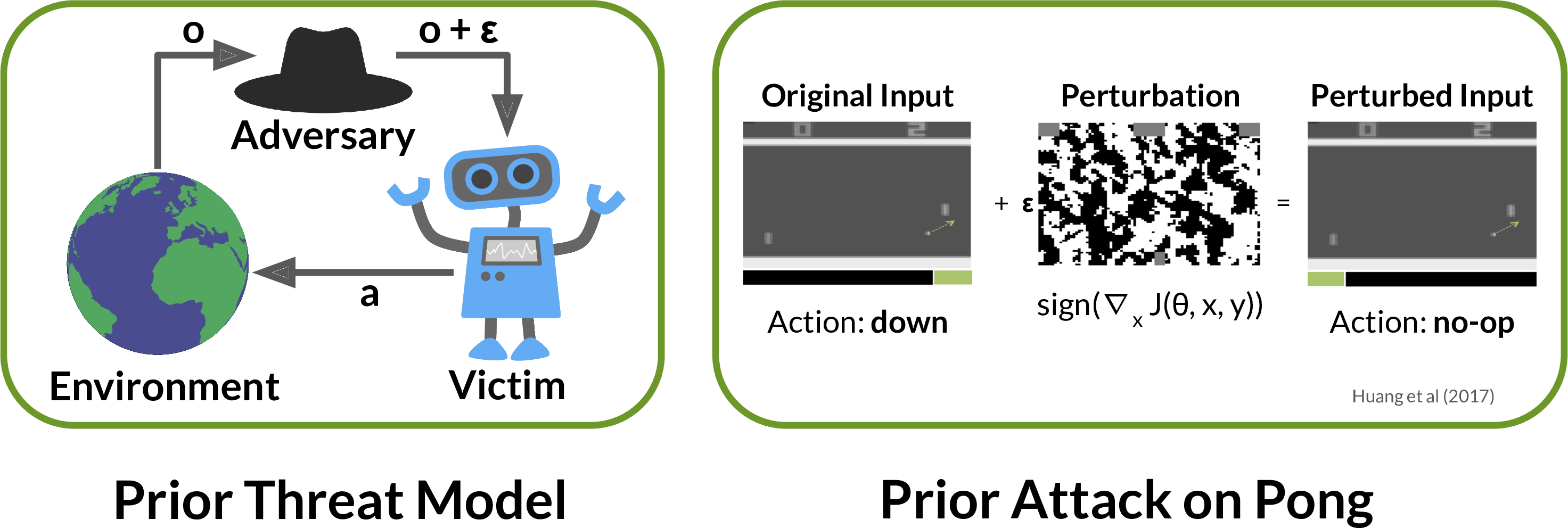
Prior work has shown deep RL policies are vulnerable to small adversarial perturbations to their observations, similar to adversarial examples in image classifiers. This threat model assumes the adversary can directly modify the victim’s sensory observation. Such low-level access is rarely possible. For example, an autonomous vehicle’s camera image can be influenced by other drivers, but only to a limited extent. Other drivers cannot add noise to arbitrary pixels, or make a building disappear.
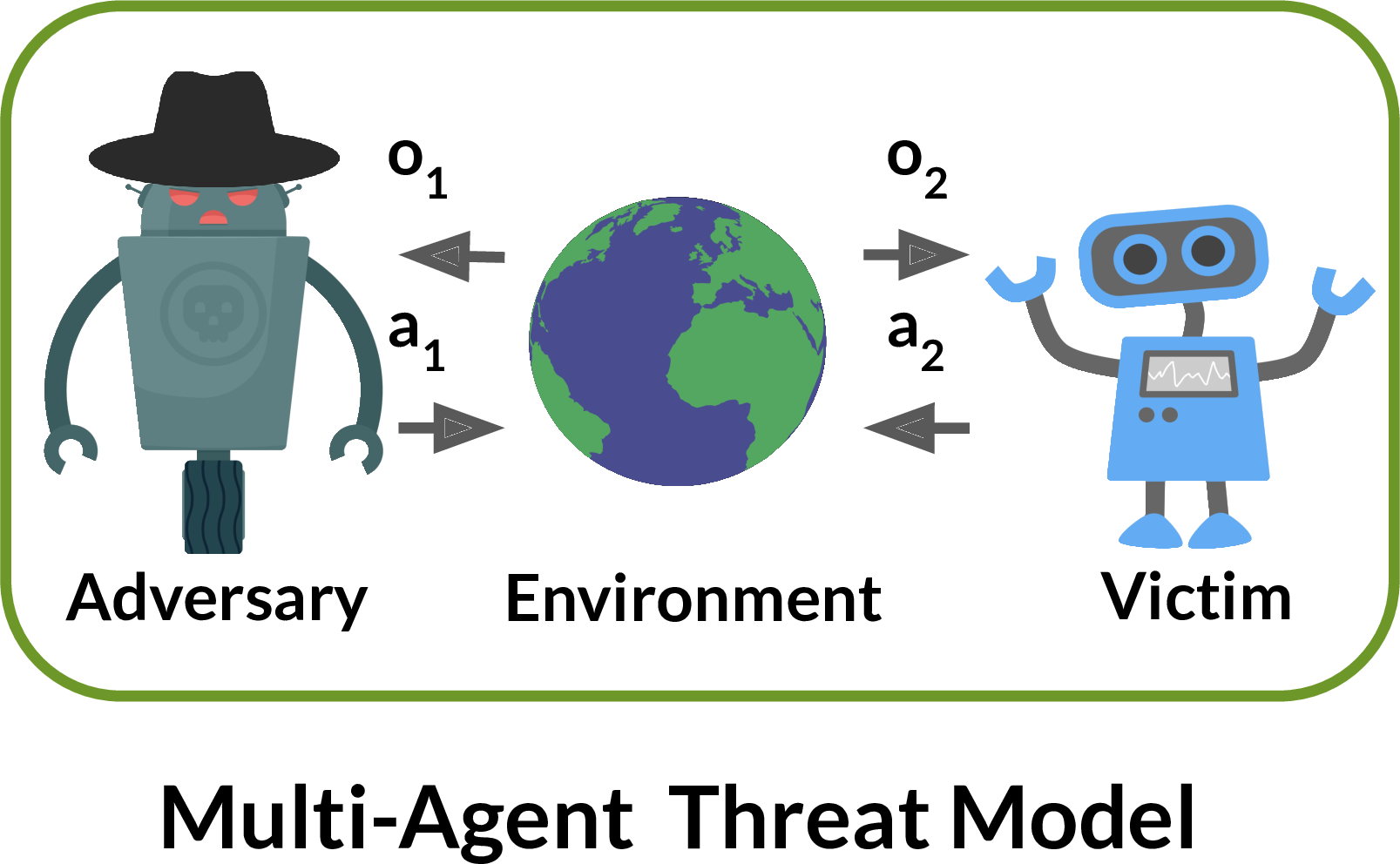
By contrast, we model the victim and adversary as agents in a shared environment. The adversary can take a similar set of actions to the victim. These actions may indirectly change the observations the victim sees, but only in a physically realistic fashion.
Note that if the victim policy were to play a Nash equilibria, it would not be exploitable by an adversary. We therefore focus on attacking victim policies trained via self-play, a popular method that approximates Nash equilibria. While it is known self-play may not always converge, it has produced highly capable AI systems. For example, AlphaGo and OpenAI Five have beaten world Go champions, and a professional Dota 2 team.
We find it is still possible to attack victim policies in this more realistic multi-agent threat model. Specifically, we exploit state-of-the-art policies trained by Bansal et al from OpenAI in zero-sum games between simulated Humanoid robots. We train our adversarial policies against a fixed victim policy, for less than 3% as many timesteps as the victim was trained for. In other respects, it is trained similarly to the self-play opponents: we use the same RL algorithm, Proximal Policy Optimization, and the same sparse reward. Surprisingly, the adversarial policies reliably beat most victims, despite not standing up and instead flailing on the ground.

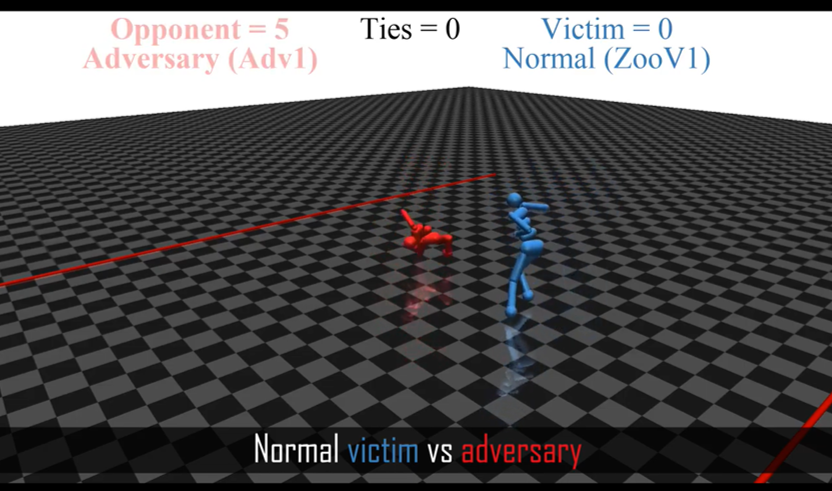
In the video at the top of the post, we show victims in three different environments playing normal self-play opponents and adversarial policies. The Kick and Defend environment is a penalty shootout between a victim kicker and goalie opponent. You Shall Not Pass has a victim runner trying to cross the finish line, and an opponent blocker trying to prevent them. Sumo Humans has two agents competing on a round arena to knock out their opponent.
In Kick and Defend and You Shall Not Pass, the adversarial policy never stands up nor touches the victim. Instead, it positions its body in such a way to cause the victim’s policy to take poor actions. This style of attack is impossible in Sumo Humans, where the adversarial policy would immediately lose if it fell over. Instead, the adversarial policy learns to kneel in the center in a stable position, which proves surprisingly effective.
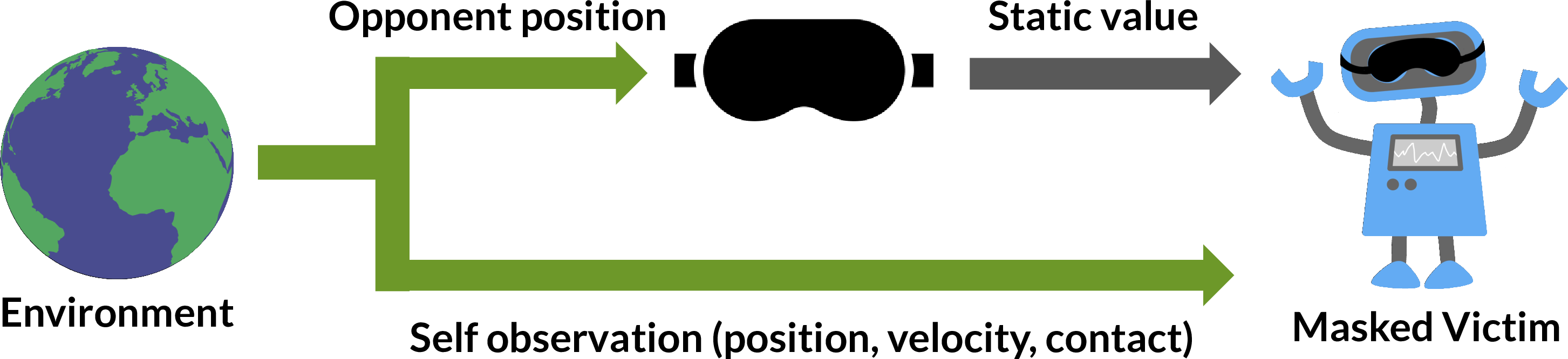
To better understand how the adversarial policies exploit their victims, we created “masked” versions of victim policies. The masked victim always observes a static value for the opponent position, corresponding to a typical initial starting state. This doctored observation is then passed to the original victim policy.
One would expect performance to degrade when the policy cannot see its opponent, and indeed the masked victims win less often against normal opponents. However, they are far more robust to adversarial policies. This result shows that the adversarial policies win by taking actions to induce natural observations that are adversarial to the victim, and not by physically interfering with the victim.
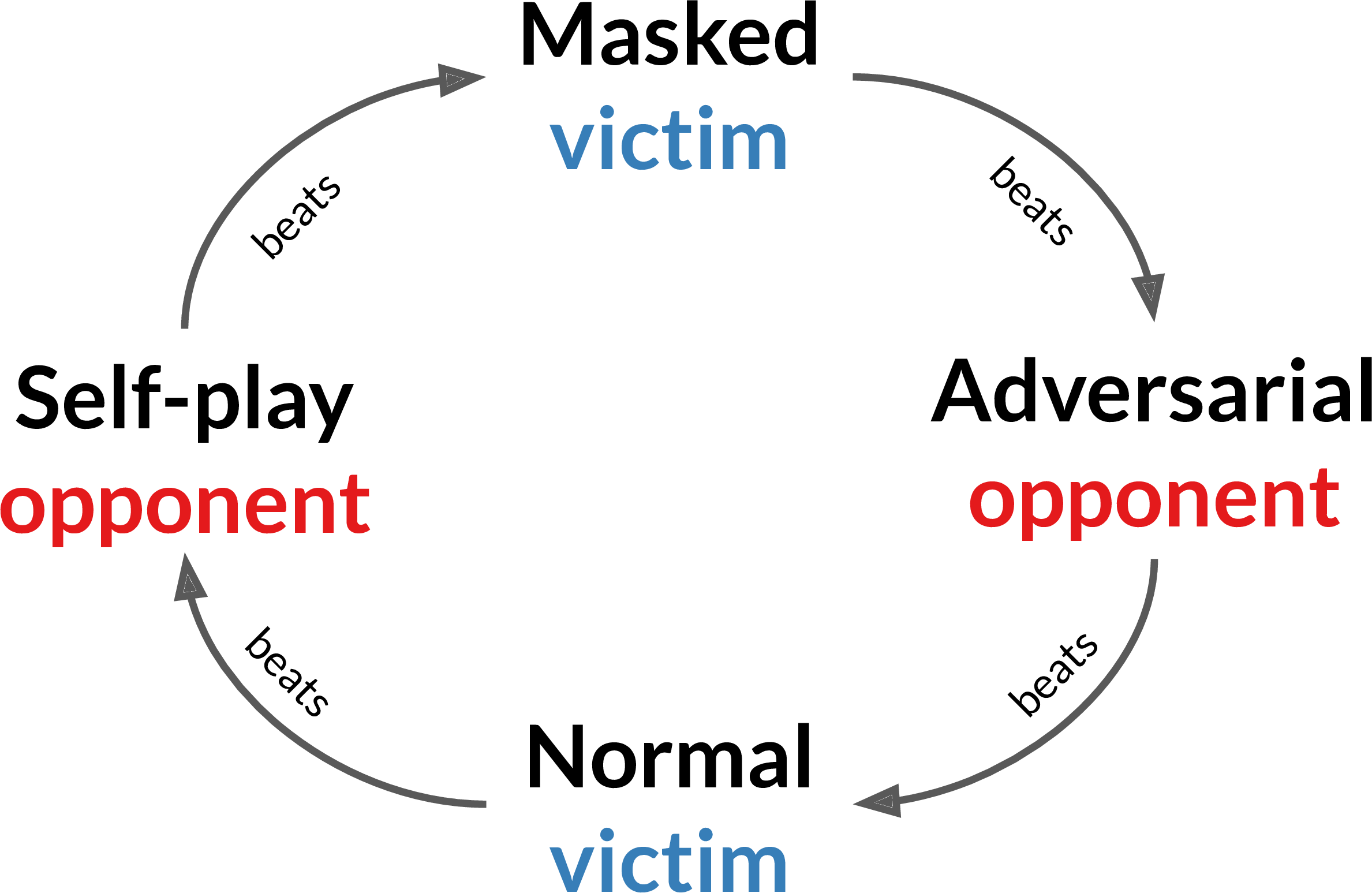
Furthermore, these results show there is a cyclic relationship between the policies. There is no overall strongest policy: the best policy depends on the other player’s policy, like in rock-paper-scissors. Technically this is known as non-transitivity: policy A beats B which beats C, yet C beats A. This is surprising since these environments’ real-world analogs are (approximately) transitive: professional human soccer players and sumo wrestlers can reliably beat amateurs. Self play assumes transitivity and so this may be why the self-play policies are vulnerable to attack.
Of course in general we don’t want to completely blind the victim, since this hurts performance against normal opponents. Instead, we propose adversarial training: fine-tuning the victim policy against the adversary that has been trained against it. Specifically, we fine-tune for 20 million timesteps, the same amount of experience the adversary is trained with. Half of the episodes are against an adversary, and the other half against a normal opponent. We find the fine-tuned victim policy is robust to the adversary it was trained against, and suffers only a small performance drop against a normal opponent.
However, one might wonder if this fine-tuned victim is robust to our attack method, or just the adversary it was fine-tuned against. Repeating the attack method finds a new adversarial policy:
Notably, the new adversary trips the victim up rather than just flailing around. This suggests our new policies are meaningfully more robust (although there may of course be failure modes we haven’t discovered).
The existence of adversarial policies has significant implications for the training, understanding and evaluation of RL policies. First, adversarial policies highlight the need to move beyond self-play. Promising approaches include iteratively applying the adversarial training defence above, and population-based training which naturally trains against a broader range of opponents.
Second, this attack shows that RL policies can be vulnerable to adversarial observations that are on the manifold of naturally occurring data. By contrast, most prior work on adversarial examples has produced physically unrealistic perturbed images.
Finally, these results highlight the limitations of current evaluation methodologies. The victim policies have strong average-case performance against a range of both normal opponents and random policies. Yet their worst-case performance against adversarial policies is extremely poor. Moreover, it would be difficult to find this worst-case by hand: the adversarial policies do not seem like challenging opponents to human eyes. We would recommend testing safety-critical policies by adversarial attack, constructively lower bounding the policies’ exploitability.
To find out more, check out our paper or visit the project website for more example videos.
This article was initially published on the BAIR blog, and appears here with the authors’ permission.









