
ΑΙhub.org
Using AI to tackle the challenge of materials structure prediction
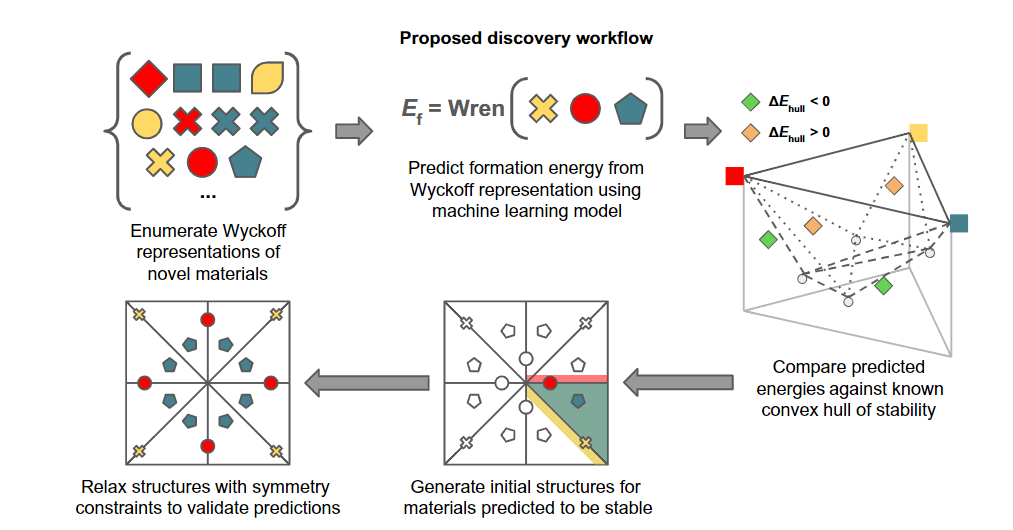 Proposed material discovery workflow. From Rapid discovery of stable materials by coordinate-free coarse graining. Image reproduced under a CC BY-NC 4.0 licence.
Proposed material discovery workflow. From Rapid discovery of stable materials by coordinate-free coarse graining. Image reproduced under a CC BY-NC 4.0 licence.
Researchers have designed a machine learning method that can predict the structure of new materials. The researchers, from Cambridge and Linköping Universities, have designed a way to predict the structure of materials given its constitutive elements. The results are reported in the journal Science Advances.
The arrangement of atoms in a material determines its properties. The ability to predict this arrangement computationally for different combinations of elements, without having to make the material in the lab, would enable researchers to quickly design and improve materials. This paves the way for advances such as better batteries and photovoltaics.
However, there are many ways that atoms can ‘pack’ into a material: some packings are stable, others are not. Determining the stability of a packing is computationally intensive, and calculating every possible arrangement of atoms to find the best one is not practical. This is a significant bottleneck in materials science.
“This materials structure prediction challenge is similar to the protein folding problem in biology,” said Dr Alpha Lee from Cambridge’s Cavendish Laboratory, who co-led the research. “There are many possible structures that a material can ‘fold’ into. Except the materials science problem is perhaps even more challenging than biology because it considers a much broader set of elements.”
Lee and his colleagues developed a method based on machine learning that successfully tackles this challenge. They developed a new way to describe materials, using the mathematics of symmetry to reduce the infinite ways that atoms can pack into materials into a finite set of possibilities. They then used machine learning to predict the ideal packing of atoms, given the elements and their relative composition in the material.
Their method accurately predicts the structure of materials that hold promise for piezoelectric and energy harvesting applications, with improved efficiency over existing models. Their method can also find thousands of new and stable materials that have never been made before, in a way that is computationally efficient.
“The number of materials that are possible is four to five orders of magnitude larger than the total number of materials that we have made since antiquity,” said co-first author Dr Rhys Goodall, also from the Cavendish Laboratory. “Our approach provides an efficient computational approach that can ‘mine’ new stable materials that have never been made before. These hypothetical materials can then be computationally screened for their functional properties.”
The researchers are now using their machine learning platform to find new functional materials such as dielectric materials. They are also integrating other aspects of experimental constraints into their materials discovery approach.
The research was supported in part by the Royal Society and the Winton Programme for the Physics of Sustainability.
Read the paper in full
Rapid discovery of stable materials by coordinate-free coarse graining
Rhys E. A. Goodall, Abhijith S. Parackal, Felix A. Faber, Rickard Armiento, Alpha A. Lee









