
ΑΙhub.org
Accelerating drug development with AI
 Rens Dimmendaal & Banjong Raksaphakdee / Medicines (flipped) / Licenced by CC-BY 4.0
Rens Dimmendaal & Banjong Raksaphakdee / Medicines (flipped) / Licenced by CC-BY 4.0
Developing new drugs to treat illnesses has typically been a slow and expensive process. However, a team of researchers at the University of Waterloo uses machine learning to speed up the development time.
The Waterloo research team has created “Imagand,” a generative artificial intelligence model that assesses existing information about potential drugs and then suggests their potential properties. Trained on and tested against existing drug data, Imagand successfully predicts important properties of different drugs that have already been independently verified in lab studies, demonstrating the AI’s accuracy.
Traditionally, bringing a successful drug candidate to market can cost between US$2 billion and US$3 billion and take over a decade to complete. Generative AI is posed to transform drug discovery by harnessing large amounts of drug data across diverse areas.
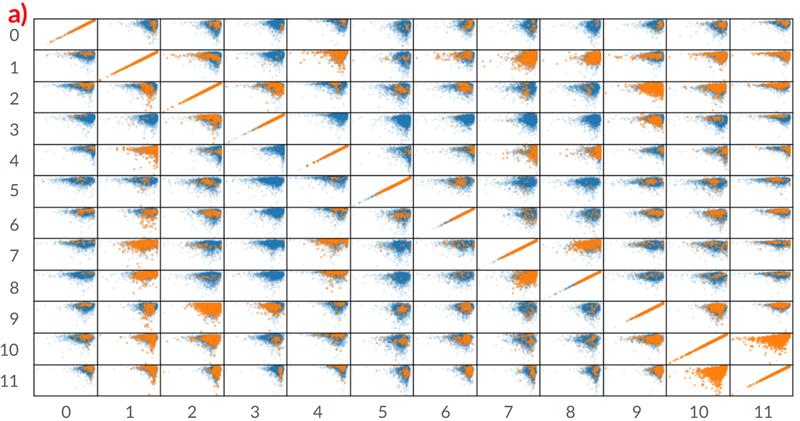 The image from the study shows a correlation between pairs of pharmacokinetic (PK) properties for a single drug. Each drug has its unique chemical profile and set of PK property values. The goal of the diagram is to show the distribution similarity between the real reported pairs of PK properties correlation from in vitro studies and those generated by the researchers’ model. This is important to show that the tool can be helpful in guiding and reducing the cost of large in vitro assays and studies to accelerate pre-clinical drug discovery.
The image from the study shows a correlation between pairs of pharmacokinetic (PK) properties for a single drug. Each drug has its unique chemical profile and set of PK property values. The goal of the diagram is to show the distribution similarity between the real reported pairs of PK properties correlation from in vitro studies and those generated by the researchers’ model. This is important to show that the tool can be helpful in guiding and reducing the cost of large in vitro assays and studies to accelerate pre-clinical drug discovery.
“There’s an enormous pool of possible chemicals and proteins to investigate when developing a new drug, which makes it very expensive to do drug discovery because you have to test millions of molecules with thousands of different targets,” said Bing Hu, a PhD candidate in Computer Science and the lead author on the research. “We are figuring out ways that AI can make that faster and cheaper.”
One of the major challenges in pharmaceutical medicine development is understanding not only how a drug might affect the body in isolation but also how it might interact with other drugs or a person’s lifestyle. This information is particularly difficult to gather because scientific studies of drugs usually only focus on the drugs’ predetermined properties, not on how they may interact with other drugs.
Ultimately, the team hopes medical researchers can use Imagand in the future to understand how drugs interact, allowing them to eliminate potential new drug candidates that would have bad side effects or interactions.
“For example, this AI-enabled process can help us understand how toxic a drug is, how it affects the heart, or how it might interact negatively with other drugs commonly used in treating an illness,” said Helen Chen, a professor in the School of Public Health Sciences and Computer Science at Waterloo. “This is one example of how AI is helping us move towards more precise, personalized care.”
The research, titled “Drug discovery SMILES-to-pharmacokinetics diffusion models with deep molecular understanding“, is currently in preprint.
tags: Focus on good health and well-being, Focus on UN SDGs









