
ΑΙhub.org
Interview with Siddharth Bhatia: a new approach for anomaly detection
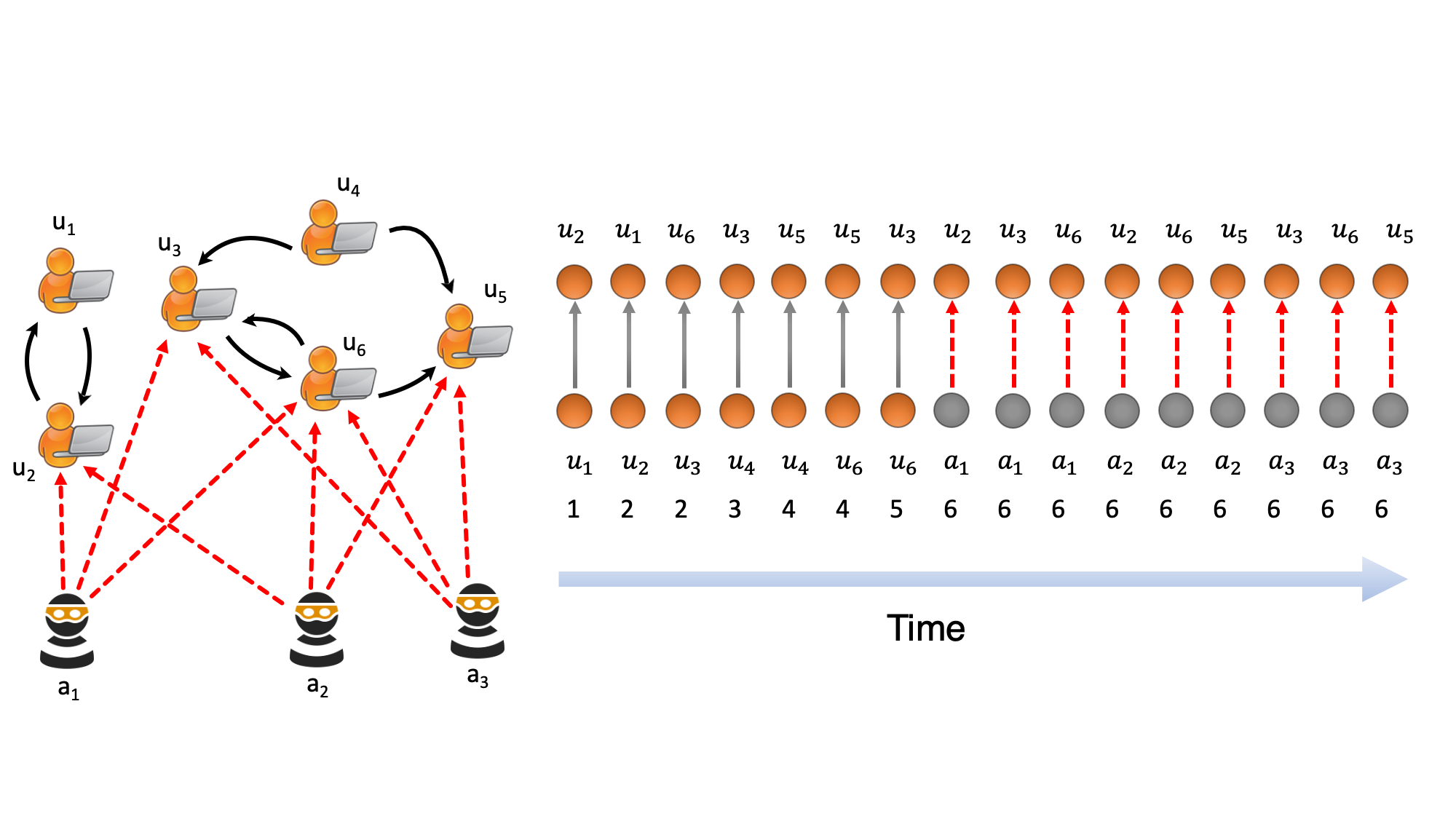
In work presented at AAAI-20 researchers from National University of Singapore, Carnegie Mellon University, and KAIST described their approach for anomaly detection in time-evolving graphs. In this interview Siddharth Bhatia tells us about their methodology, why research into anomaly detection is crucial, and plans for future studies.
What is topic of the research in your paper?
Anomaly detection in graphs is a critical problem for finding suspicious behavior in innumerable systems, such as intrusion detection, fake ratings, and financial fraud. This has been a well-researched problem with the majority of the proposed approaches focusing on static graphs. However, many real-world graphs are dynamic in nature, and methods based on static connections may miss temporal characteristics of the graphs and anomalies.
Among the methods focusing on dynamic graphs, most of them have edges aggregated into graph snapshots. However, to minimize the effect of malicious activities and start recovery as soon as possible, we need to detect anomalies in real-time or near real-time i.e. to identify whether an incoming edge is anomalous or not, as soon as we receive it. In addition, since the number of vertices can increase as we process the stream of edges, we need an algorithm which uses constant memory in the graph size. Moreover, fraudulent or anomalous events in many applications occur in microclusters or suddenly arriving groups of suspiciously similar edges e.g. denial of service attacks in network traffic data and lockstep behavior.
MIDAS, short for Microcluster-Based Detector of Anomalies in Edge Streams, detects microcluster anomalies, or suddenly arriving groups of suspiciously similar edges, in edge streams, using constant time and memory. In addition, by using a principled hypothesis testing framework, MIDAS provides theoretical bounds on the false positive probability, which earlier methods do not provide. Also, MIDAS is up to 48% more accurate while being up to 644 times faster than state of the art approaches.
Could you tell us a little bit about the implications of your research and why it is an interesting area for study?
MIDAS finds anomalies or malicious entities in time-evolving graphs. MIDAS can be used to detect intrusions, Denial of Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. It can also be used to detect fake profiles in Social Networks like Twitter, Facebook, Amazon reviews, and Financial Frauds. MIDAS requires constant memory to detect these anomalies in real-time so as to minimize the harm caused by them.
Could you explain your methodology?
MIDAS finds anomalous edges from a dynamic graph in a streaming manner. It combines a chi-squared goodness-of-fit test with the Count-Min-Sketch (CMS) streaming data structures to get an anomaly score for each edge. MIDAS also incorporates temporal and spatial relations to achieve better performance.
What were your main findings?
1. MIDAS detects Microcluster Anomalies i.e. suddenly arriving groups of suspiciously similar edges.
2. We give theoretical Guarantees on the False Positive Probability.
3. MIDAS requires constant memory and is independent of the graph size.
4. MIDAS takes constant update time for each edge. This allows for real-time anomaly detection.
5. MIDAS is scalable and can process up to 4 million edges in less than 1 second on a normal laptop.
6. MIDAS is up to 48% more accurate and 644 times faster than the state of the art approaches.
What further work are you planning in this area?
Different developers have implemented MIDAS in Python, Ruby, Rust, R, and Golang in addition to the C++ version we originally released. MIDAS source code and different implementations are open source, and available on the Github project page.
MIDAS is currently being deployed in real-world systems to improve their performance. Different cybersecurity firms have also asked us to tune MIDAS according to their requirements.
We have extended MIDAS to MStream: Fast Streaming Multi-Aspect Group Anomaly Detection. In MStream, we detect anomalies on high dimensional multi-aspect data having both categorical and numeric attributes. We demonstrate how MStream outperforms several baselines including popular scikit-learn algorithms like Isolation Forest and Local Outlier Factor in terms of both accuracy and running time. We are also looking to incorporate Deep Learning based methods to further improve performance.
Read the article in full
MIDAS: Microcluster-Based Detector of Anomalies in Edge Streams
Siddharth Bhatia, Bryan Hooi, Minji Yoon, Kijung Shin, Christos Faloutsos
Code and project page
The code is available here.
About the author
 Siddharth Bhatia is a Ph.D. student at the National University of Singapore (NUS) advised by Bryan Hooi. His research is in Streaming Anomaly Detection. At NUS, he is supported by a Presidents Graduate Fellowship. Before joining NUS, Siddharth completed his undergraduate and master’s degrees from BITS Pilani. Siddharth has previously been recognized as a Young Researcher in the ACM Heidelberg Laureate Forum. He will be applying his research at Amazon Web Services (AWS) this summer. Access his webpage here.
Siddharth Bhatia is a Ph.D. student at the National University of Singapore (NUS) advised by Bryan Hooi. His research is in Streaming Anomaly Detection. At NUS, he is supported by a Presidents Graduate Fellowship. Before joining NUS, Siddharth completed his undergraduate and master’s degrees from BITS Pilani. Siddharth has previously been recognized as a Young Researcher in the ACM Heidelberg Laureate Forum. He will be applying his research at Amazon Web Services (AWS) this summer. Access his webpage here.
tags: AAAI, AAAI2020









